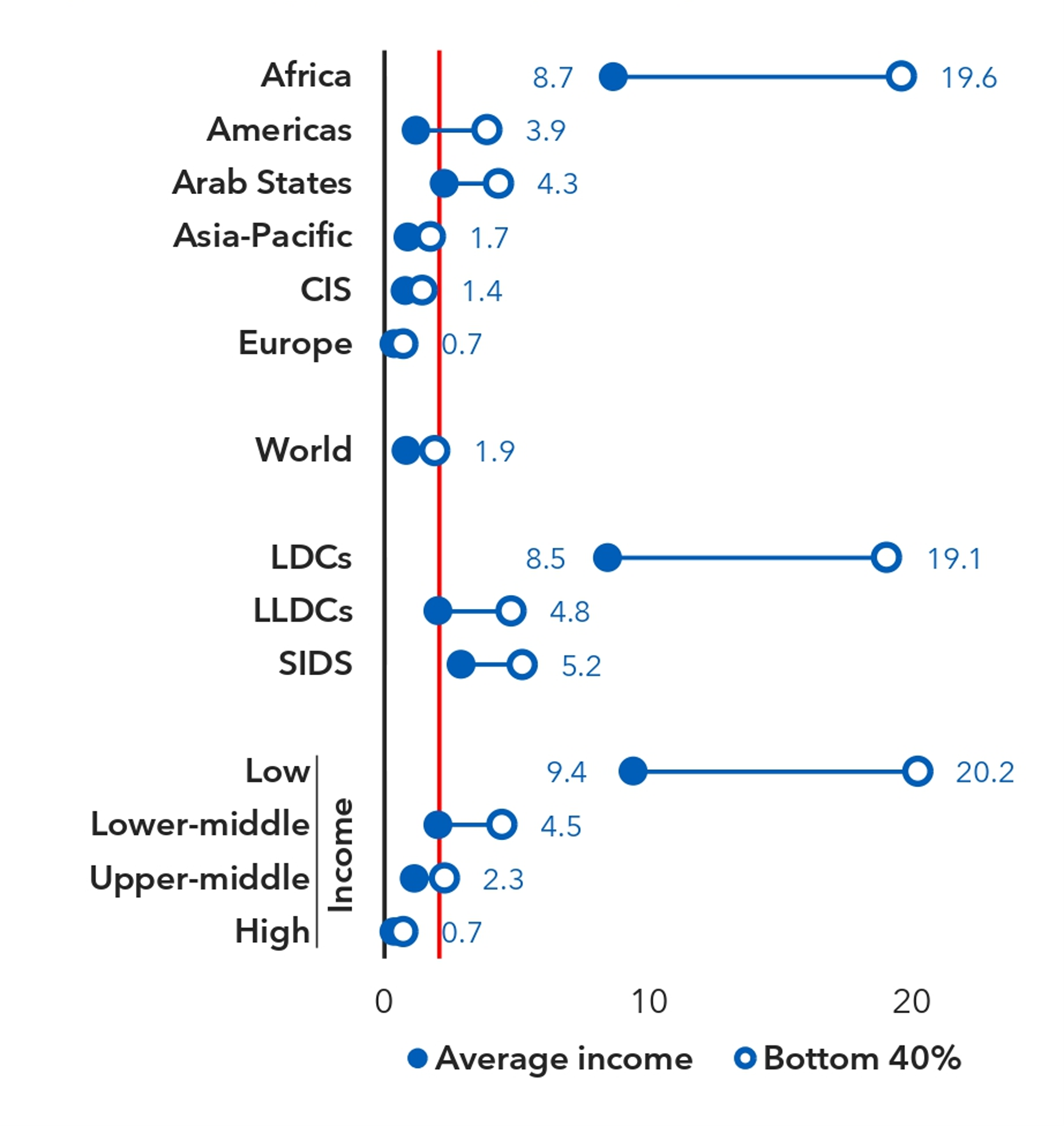
There are affordability gaps not only between high- and low-income economies, but also within countries.
ITU price statistics combined with inequality data from the World Bank, published in the Global Connectivity Report 2025 (figure 4.6), reveal wide gaps between how much a mobile broadband basket amounts to those earning the average income, and those among the poorest 40 per cent of the population.
Note: Based on 107 countries with available recent inequality survey data (not older than 2019) and price data (2025).
Source: World Bank PIP, ITU.