
Greening digital technologies
Digital technologies play a key role in climate action, but their growing environmental footprint is a concern. ITU works with partners to drive sustainable digital transformation worldwide, from reducing emissions and e-waste, to setting green standards and more.
Digital technologies make us more productive and reduce our carbon footprint in many ways. Yet, as we increasingly rely on digital technologies, the environmental impact becomes more pronounced. The digital sector is now responsible for up to 4% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and generates 62 billion kilograms of e-waste annually.
The rapid growth of emerging technologies, such as AI and cloud computing, has further amplified demands on energy, water, and material consumption. The computing power required for AI alone is doubling every 100 days, driving energy demands to grow by 26-36% annually.
Tackling these challenges requires a collective commitment to building a sustainable digital future.


Fast-track partnerships
ITU has been highlighting the connection between telecommunications and the environment since the 1970s. In 1994, before the first UN Climate Change Conference, ITU’s Kyoto Plenipotentiary Conference called for action to ensure telecommunications and digital technologies contribute to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Since then, ITU has worked closely with its membership across radiocommunication, development, and standardization to ensure digital technologies positively contribute to climate action.
The international community is rising to the challenge. ITU’s Green Digital Action initiative has become a driving force for global collaboration, uniting stakeholders to develop tangible commitments, scalable solutions, and strong global monitoring.
At the 2024 UN Climate Conference in Baku, Azerbaijan, over 1,800 companies and organizations, alongside 82 countries, endorsed the COP29 Declaration on Green Digital Action, reaffirming a shared commitment to reduce the environmental footprint of the digital sector while accelerating climate solutions across economies.
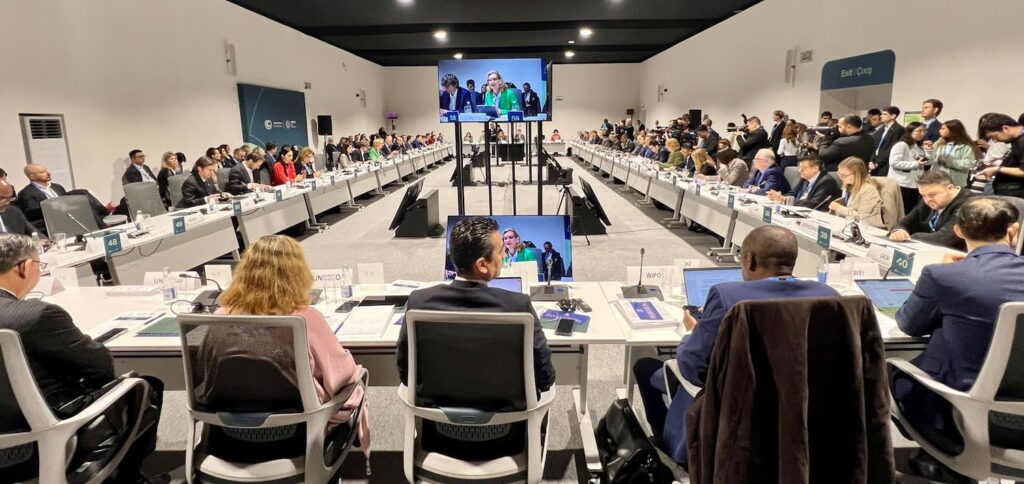


In 2025, this commitment moved into a new phase of delivery. At COP30 in Belém, Brazil, ITU and partners announced the creation of the Green Digital Action Hub, a new cooperation platform anchored in Brazil as a lasting legacy of the conference. Designed as the nerve centre of Green Digital Action, the hub aims to accelerate innovation, strengthen data and measurement, and support countries, particularly in the Global South, in scaling green digital solutions within and beyond the technology sector.
Additionally at COP30, ITU launched a stocktake providing the first global snapshot of where digitalization stands in Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) with 2035 targets. The analysis of 53 NDCs found that almost almost 90% of the NDCs reference digital technologies as implementation levers. At the same time, most NDCs only account for digital technologies as part of specific solutions to achieve sectoral targets and the digital sector is not regarded as a sector in its own right with separate mitigation and adaptation targets to account for its own impact. Stay tuned for the complete NDC analysis in 2026.

A sustainable digital ecosystem
A sustainable digital future requires embedding sustainability throughout the entire digital lifecycle.
ITU supports countries in reducing emissions, harnessing climate monitoring technologies, and building green digital ecosystems. This includes advancing energy-efficient networks and data centres, promoting smart energy and circularity, and strengthening climate adaptation and digital resilience.
1. Sustainable by design: Establishing green standards
Standards are the cornerstone of sustainable innovation, guiding the ICT sector to improve energy efficiency, reduce CO2 emissions, and enable meaningful reporting and comparisons.
Key ITU activities include:
- Development of green ICT standards (ITU-T SG5 – Environment, EMF, Climate Action and Circular Economy)
- Guidance on measuring GHG emissions and broader environmental impacts in the ICT sector, including methodologies for assessing scope 3 emissions
- Development of standards that support AI’s environmental efficiency, including ITU-T L.1801 – Guidelines for Assessing the Environmental Impact of Artificial Intelligence Systems, a landmark standard for evaluating the environmental footprint of AI
- Promoting lifecycle assessment and environmental efficiency monitoring of ICT infrastructure and networks
- Advancing methodologies to measure the enablement effect of ICT solutions across sectors (ITU-T L.1480)
- Enabling the use of ICT to decarbonize other sectors through sector-specific standards
ITU standards ensure that sustainability is built into every product and service from the ground up, driving informed decisions across the value chain


2. Strengthening green capacity building and adoption
Standards need adoption to make an impact. ITU strengthens capacity by equipping stakeholders with the knowledge, tools, and skills to implement environmentally sustainable ICT practices.
Key ITU activities include:
- Capacity building and training through ITU Academy online courses on ICT & climate change and e-waste
- Guidelines for Green Data Centers
- Global forums and knowledge-sharing platforms, including Green Standards Week and symposia on ICTs, environment, and climate change
ITU works to ensure stakeholders across industries have the resources to operationalize sustainability.
3. Monitoring, reporting, and reducing emissions
Once green practices are in place, monitoring and reporting are essential for accountability and continuous improvement. ITU’s global framework helps track emissions and set reduction targets.
Key ITU activities include:
- Development of methodologies to assess greenhouse gas emissions trajectories of the ICT sector (ITU-T L.1470)
- Guidance for ICT Companies setting science based emission reduction targets.
- Scope 3 Guidance for Telecommunication operators
- Annual progress reporting through the yearly Greening Digital Companies Report 2025 by ITU and the World Benchmarking Alliance and the accompanying Greening Digital Dashboard
- Gathering and disseminating data on GHG emissions and energy use within the ICT sector, at the national level
ITU works to promote transparency and enable measurable progress in reducing the sector’s environmental footprint.


4. Leveraging digital technologies for climate monitoring
With robust emissions data and monitoring in place, digital technologies such as remove sensing and Earth observation can be deployed to address climate challenges. These tools provide vital data for weather prediction, disaster response, and climate change mitigation.
Key ITU outputs are ITU-R recommendations, reports and handbooks to assure the necessary performance and quality in operating of radiocommunication systems ( ITU-R Study Group 7).
ITU-R provides life blood for development of any radiocommunication system and its work is paramount to the successful operation of any radio application. Availability of radio frequency bands free from harmful interference is a requirement for the development of all Earth observation and meteorological radiosystems.
5. Enabling a circular economy for electronics
To further reduce the sector’s environmental footprint, ITU promotes a circular economy approach where electronics are reused and recycled rather than discarded.
Key ITU activities include:
- Standards supporting the circular economy, including material reduction, circular design, extended producer responsibility (EPR), digital product passports, and sustainable procurement
- Guidelines for sustainable e-waste management across the lifecycle (e.g., ITU standards L.1000 – L.1199 – E-waste and circular economy)
- E-waste monitoring through the Global E-waste Monitor
- Technical assistance to develop and implement national e-waste policy and regulation
- Guidance on circular and sustainable public procurement for ICT products.
This approach reduces waste, recovers valuable materials, and creates green job opportunities, aligning the digital sector with global sustainability goals.

6. Supporting Member States in building green digital ecosystems
To ensure no one is left behind, ITU works closely with governments and stakeholders to create customized solutions that balance economic, social, and environmental priorities.
Key ITU activities include:
- Technical assistance for e-waste policy and regulation development
- Training programs and resources to elevate green ICT practices globally (E-waste Policy and Regulation)
- Advocacy for sustainable digital transformation at regional and national levels
- Bridging the standardization gap through training, with a special focus on engaging in the development of environmental sustainability standards
By empowering countries with tailored tools and strategies, ITU helps drive a global movement toward sustainability.

A collective commitment
Shaping our sustainable digital future together
Digital technologies are key to accelerating climate action and ITU is leading the charge to bring governments, industry, civil society, and academia together to position the entire ICT sector as a leader in climate action. You too can play your part!
Get involved with the Green Digital Action initiative and guide global efforts to transform how technology, including AI, is built, used, and recycled. Email green@itu.int to learn more.