Page 95 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2024
P. 95
Innovation and Digital Transformation for a Sustainable World
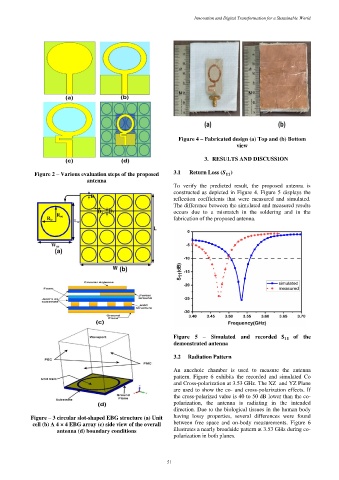
Figure 4 – Fabricated design (a) Top and (b) Bottom
view
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Figure 2 – Various evaluation steps of the proposed 3.1 Return Loss ( )
antenna
To verify the predicted result, the proposed antenna is
constructed as depicted in Figure 4. Figure 5 displays the
reflection coefficients that were measured and simulated.
The difference between the simulated and measured results
occurs due to a mismatch in the soldering and in the
fabrication of the proposed antenna.
Figure 5 – Simulated and recorded of the
demonstrated antenna
3.2 Radiation Pattern
An anechoic chamber is used to measure the antenna
pattern. Figure 6 exhibits the recorded and simulated Co
and Cross-polarization at 3.53 GHz. The XZ and YZ Plane
are used to show the co- and cross-polarization effects. If
the cross-polarized value is 40 to 50 dB lower than the co-
polarization, the antenna is radiating in the intended
direction. Due to the biological tissues in the human body
Figure – 3 circular slot-shaped EBG structure (a) Unit having lossy properties, several differences were found
cell (b) A 4 × 4 EBG array (c) side view of the overall between free space and on-body measurements. Figure 6
antenna (d) boundary conditions illustrates a nearly broadside pattern at 3.53 GHz during co-
polarization in both planes.
– 51 –