Page 26 - Methodology for measurement of Quality of Service (QoS) Key Performance Performance
Indicators (KPIs) for Digital Financial Services
P. 26
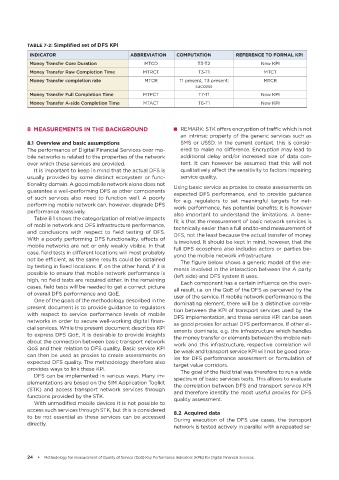
TABLE 7-2: Simplified set of DFS KPI
INDICATOR ABBREVIATION COMPUTATION REFERENCE TO FORMAL KPI
Money Transfer Core Duration MTCD T3-T2 New KPI
Money Transfer Raw Completion Time MTRCT T3-T1 MTCT
Money Transfer completion rate MTCR T1 present, T3 present: MTCR
success
Money Transfer Full Completion Time MTFCT T7-T1 New KPI
Money Transfer A-side Completion Time MTACT T6-T1 New KPI
8 MEASUREMENTS IN THE BACKGROUND ■ REMARK: STK offers encryption of traffic which is not
an intrinsic property of the generic services such as
8.1 Overview and basic assumptions SMS or USSD. In the current context, this is consid-
The performance of Digital Financial Services over mo- ered to make no difference. Encryption may lead to
bile networks is related to the properties of the network additional delay and/or increased size of data con-
over which these services are provided. tent. It can however be assumed that this will not
It is important to keep in mind that the actual DFS is qualitatively affect the sensitivity to factors impairing
usually provided by some distinct ecosystem or func- service quality.
tionality domain. A good mobile network alone does not Using basic service as proxies to create assessments on
guarantee a well-performing DFS as other components expected DFS performance, and to provide guidance
of such services also need to function well. A poorly for e.g. regulators to set meaningful targets for net-
performing mobile network can, however, degrade DFS work performance, has potential benefits; it is however
performance massively. also important to understand the limitations. A bene-
Table 8 1 shows the categorization of relative impacts fit is that the measurement of basic network services is
of mobile network and DFS infrastructure performance, technically easier than a full end.to-end measurement of
and conclusions with respect to field testing of DFS. DFS, not the least because the actual transfer of money
With a poorly performing DFS functionality, effects of is involved. It should be kept in mind, however, that the
mobile networks are not or only weakly visible. In that full DFS ecosphere also includes actors or parties be-
case, field tests in different locations will most probably yond the mobile network infrastructure.
not be efficient, as the same results could be obtained The figure below shows a generic model of the ele-
by testing in fixed locations. If, on the other hand, if it is ments involved in the interaction between the A party
possible to ensure that mobile network performance is (left side) and DFS system it uses.
high, no field tests are required either. In the remaining Each component has a certain influence on the over-
cases, field tests will be needed to get a correct picture all result, i.e. on the QoE of the DFS as perceived by the
of overall DFS performance and QoE. user of the service. If mobile network performance is the
One of the goals of the methodology described in the dominating element, there will be a distinctive correla-
present document is to provide guidance to regulators tion between the KPI of transport services used by the
with respect to service performance levels of mobile DFS implementation, and these service KPI can be seen
networks in order to secure well-working digital finan- as good proxies for actual DFS performance. If other el-
cial services. While the present document describes KPI ements dominate, e.g. the infrastructure which handles
to express DFS QoE, it is desirable to provide insights the money transfer or elements between the mobile net-
about the connection between basic transport network work and this infrastructure, respective correlation will
QoS and their relation to DFS quality. Basic service KPI be weak and transport service KPI will not be good prox-
can then be used as proxies to create assessments on ies for DFS performance assessment or formulation of
expected DFS quality. The methodology therefore also target value corridors.
provides ways to link these KPI. The goal of the field trial was therefore to run a wide
DFS can be implemented in various ways. Many im- spectrum of basic services tests. This allows to evaluate
plementations are based on the SIM Application Toolkit the correlation between DFS and transport service KPI
(STK) and access transport network services through and therefore identify the most useful proxies for DFS
functions provided by the STK. quality assessment.
With unmodified mobile devices it is not possible to
access such services through STK, but this is considered 8.2 Acquired data
to be not essential as these services can be accessed During execution of the DFS use cases, the transport
directly.
network is tested actively in parallel with a repeated se-
24 • Methodology for measurement of Quality of Service (QoS) Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Digital Financial Services