Page 678 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 678
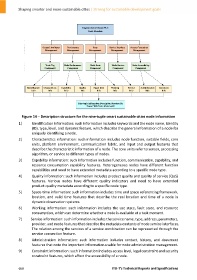
Figure 14 – Description structure for the nine‐tuple smart sustainable cities node information
1) Identification information: such information includes keywords and the node name, identity
(ID), type, level, and dynamic feature, which describe the general information of a node for
uniquely identifying a node.
2) Characteristics information: such information includes node function, suitable fields, core
units, platform environment, communication fabric, and input and output features that
describe the characteristic information of a node. The core units refer to sensor, processing
algorithm, or service to different types of nodes.
3) Capability information: such information includes function, communication, capability, and
resource consumption capability features. Heterogeneous nodes have different function
capabilities and need to have extended metadata according to a specific node type.
4) Quality information: such information includes product quality and quality of service (QoS)
features. Various nodes have different quality indicators and need to have extended
product quality metadata according to a specific node type.
5) Space‐time information: such information includes time and space referencing framework,
location, and valid time features that describe the real location and time of a node in
dynamic observation systems.
6) Working information: such information includes the use state, fault state, and resource
consumption, which can determine whether a node is available at a task moment.
7) Service information: such information includes the service name, type, address, parameters,
provider, and mode features that describe the metadata contents of node service interfaces.
The relation among the services of a service combination can be represented through the
service connection feature.
8) Administration information: such information includes contact, history, and document
features that note the important information usable for node administration management.
9) Constraint information: such information includes access level, legal constraint and security
constraint features, which affect the accessibility of a node.
668 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications