Page 676 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 676
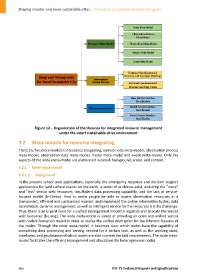
Figure 12 – Organization of the theories for integrated resource management
under the smart sustainable cities environment
3.2 Meta‐models for resource integrating
There are five meta‐models for resource integrating, namely node meta‐model, observation process
meta‐model, observation data meta‐model, model meta‐model and event meta‐model. Only the
aspects of the node meta‐model are elaborated in detail: background, scope, and content.
3.2.1 Node meta‐model
3.2.1.1 Background
In the present sensor web applications, especially the emergency response and decision support
applications for land surface events on the earth, a series of problems exist, including the "more"
and "less" sensor web resources, insufficient data processing capability, and the lack of service‐
focused model [b‐Chena]. How to make people be able to access observation resources in a
transparent, efficient and customized manner, and implement the online information fusion, data
assimilation, dynamic management, as well as intelligent service for the resources is still a challenge.
Thus, there is an urgent need for a unified management model to organize and allocate the sensor
web resources [b‐Liang]. The node meta‐model is aimed at providing an open and unified sensor
web node information model in order to realize the unified description for the inherent features of
the nodes. Through the node meta‐model, it becomes clear which nodes have the capability of
completing data processing and serving needed for a certain task, as well as the working state,
timeliness, and geolocation of which nodes are able to meet the task requirements. The node meta‐
model facilitates the efficient management and allocations for heterogeneous nodes.
666 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications