Page 673 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 673
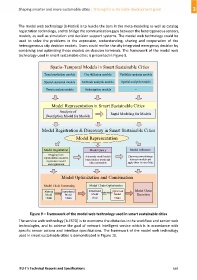
The model web technology [b‐Nativi] is to hurdle the bars in the meta‐modeling as well as catalog
registration technology, and to bridge the communication gaps between the heterogeneous sensors,
models, as well as simulation and decision support systems. The model web technology could be
used to solve the problems in the expression, understanding, sharing and cooperation of the
heterogeneous city decision models. Users could realize the city integrated emergency decision by
combining and optimizing these models on decision terminals. The framework of the model web
technology used in smart sustainable cities is presented in Figure 9.
Spatio-Temporal Models in Smart Sustainable Cities
Trend prediction models Gas diffusion models Visibility analysis models
Spatial statistical models Network analysis models Spatial analysis models
Terrain analysis models Optimization models ...
Model Representation in Smart Sustainable Cities
Analysis of
Description Model for Models Rapid Modeling for Models
Model Registration & Discovery in Smart Sustainable Cities
Model Representation
Model Registration Model Query Model Inference
Mapping from
representation model to Automatic model match Discover new relations
between models and
registration model based on key words and apply them in new fields
and registration other constraints
Model Optimization and Combination
Model Chain Generating Model Chain Optimization
Abstract Instantiation Instantiated Instantiated Optimization Optimized Model Chain
Model Model Model Model Execution
Chain Chain Chain Chain
Figure 9 – Framework of the model web technology used in smart sustainable cities
The service web technology [b‐ESTO] is to overcome the obstacles in the workflow and sensor web
technologies, and to achieve the goal of network intelligent service which is in accordance with
specific sensor actions and interface specifications. The framework of the model web technology
used in smart sustainable cities is demonstrated in Figure 10.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 663