Page 675 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 675
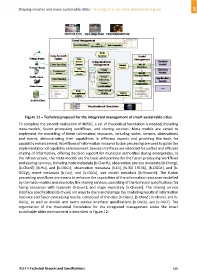
Figure 11 – Technical proposal for the integrated management of smart sustainable cities
To complete the smooth realization of IMSSC, a set of theoretical foundation is needed, including
meta‐models, fusion processing workflows, and sharing services. Meta‐models are aimed to
implement the modelling of these information resources, including nodes, sensors, observations
and events, demonstrating their capabilities in different aspects and providing the basis for
capability enhancement. Workflows of information resource fusion processing are used to guide the
implementation of capability enhancement. Service interfaces are intended for unified and efficient
sharing of information, offering decision support for municipal authorities during emergencies. In
the infrastructure, the meta‐models are the basis and premise for the fusion processing workflows
and sharing services, including node metadata [b‐Chenh]; observation process metadata [b‐Cheng],
[b‐Chenf], [b‐Hu], and [b‐OGCc]; observation metadata [b‐Di], [b‐ISO 19156], [b‐OGCd], and [b‐
OGCg]; event metadata [b‐Fan], and [b‐OGCe], and model metadata [b‐Visconti]. The fusion
processing workflows are means to enhance the capabilities of the information resources modelled
by the meta‐models and shared by the sharing services, consisting of the technical specifications for
fusing resources with toponym [b‐Smart], and maps separately [b‐Chanier]. The sharing service
interface specifications [b‐Chenb] are ways to share and manage the modelling results of information
resource and fusion processing results, composed of the data [b‐Chenc], [b‐Chend], [b‐Chene], and [b‐
OGCa], as well as model, and event service interface specifications [b‐OGCb], and [b‐OGCf]. The
organization of the theoretical foundation for the integrated management under the smart
sustainable cities environment is described in Figure 12:
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 665