Page 215 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2024
P. 215
Innovation and Digital Transformation for a Sustainable World
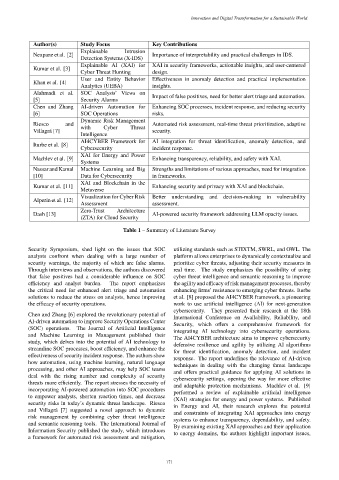
Author(s) Study Focus Key Contributions
Explainable Intrusion
Neupane et al. [2] Importance of interpretability and practical challenges in IDS.
Detection Systems (X-IDS)
Explainable AI (XAI) for XAI in security frameworks, actionable insights, and user-centered
Kumar et al. [3]
Cyber Threat Hunting design.
User and Entity Behavior Effectiveness in anomaly detection and practical implementation
Khan et al. [4]
Analytics (UEBA) insights.
Alahmadi et al. SOC Analysts’ Views on Impact of false positives, need for better alert triage and automation.
[5] Security Alarms
Chen and Zhang AI-driven Automation for Enhancing SOC processes, incident response, and reducing security
[6] SOC Operations risks.
Dynamic Risk Management
Riesco and with Cyber Threat Automated risk assessment, real-time threat prioritization, adaptive
Villagrá [7] security.
Intelligence
AI4CYBER Framework for AI integration for threat identification, anomaly detection, and
Iturbe et al. [8]
Cybersecurity incident response.
XAI for Energy and Power
Machlev et al. [9] Enhancing transparency, reliability, and safety with XAI.
Systems
Nassar and Kamal Machine Learning and Big Strengths and limitations of various approaches, need for integration
[10] Data for Cybersecurity in frameworks.
XAI and Blockchain in the
Kumar et al. [11] Enhancing security and privacy with XAI and blockchain.
Metaverse
Visualization for Cyber Risk Better understanding and decision-making in vulnerability
Alperin et al. [12]
Assessment assessment.
Zero-Trust Architecture
Dash [13] AI-powered security framework addressing LLM opacity issues.
(ZTA) for Cloud Security
Table 1 – Summary of Literature Survey
Security Symposium, shed light on the issues that SOC utilizing standards such as STIXTM, SWRL, and OWL. The
analysts confront when dealing with a large number of platform allows enterprises to dynamically contextualize and
security warnings, the majority of which are false alarms. prioritize cyber threats, adjusting their security measures in
Through interviews and observations, the authors discovered real time. The study emphasizes the possibility of using
that false positives had a considerable influence on SOC cyber threat intelligence and semantic reasoning to improve
efficiency and analyst burden. The report emphasizes the agility and efficacy of risk management processes, thereby
the critical need for enhanced alert triage and automation enhancing firms’ resistance to emerging cyber threats. Iturbe
solutions to reduce the stress on analysts, hence improving et al. [8] proposed the AI4CYBER framework, a pioneering
the efficacy of security operations. work to use artificial intelligence (AI) for next-generation
cybersecurity. They presented their research at the 18th
Chen and Zhang [6] explored the revolutionary potential of International Conference on Availability, Reliability, and
AI-driven automation to improve Security Operations Center Security, which offers a comprehensive framework for
(SOC) operations. The Journal of Artificial Intelligence integrating AI technology into cybersecurity operations.
and Machine Learning in Management published their The AI4CYBER architecture aims to improve cybersecurity
study, which delves into the potential of AI technology to defensive resilience and agility by utilizing AI algorithms
streamline SOC processes, boost efficiency, and enhance the for threat identification, anomaly detection, and incident
effectiveness of security incident response. The authors show response. The report underlines the relevance of AI-driven
how automation, using machine learning, natural language techniques in dealing with the changing threat landscape
processing, and other AI approaches, may help SOC teams and offers practical guidance for applying AI solutions in
deal with the rising number and complexity of security cybersecurity settings, opening the way for more effective
threats more efficiently. The report stresses the necessity of and adaptable protection mechanisms. Machlev et al. [9]
incorporating AI-powered automation into SOC procedures performed a review of explainable artificial intelligence
to empower analysts, shorten reaction times, and decrease (XAI) strategies for energy and power systems. Published
security risks in today’s dynamic threat landscape. Riesco in Energy and AI, their research explores the potential
and Villagrá [7] suggested a novel approach to dynamic and constraints of integrating XAI approaches into energy
risk management by combining cyber threat intelligence systems to enhance transparency, dependability, and safety.
and semantic reasoning tools. The International Journal of By examining existing XAI approaches and their application
Information Security published the study, which introduces to energy domains, the authors highlight important issues,
a framework for automated risk assessment and mitigation,
– 171 –