Page 34 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5 – Internet of Everything
P. 34
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5
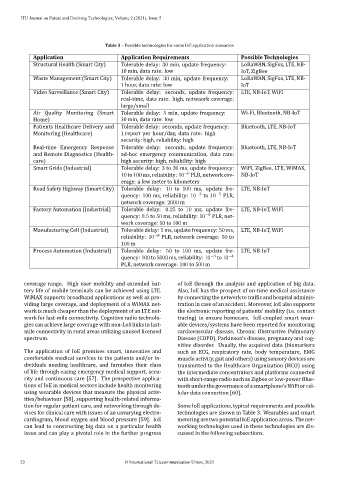
Table 3 – Possible technologies for some IoE application scenarios
Application Application Requirements Possible Technologies
Structural Health (Smart City) Tolerable delay: 30 min, update frequency: LoRaWAN, SigFox, LTE, NB‑
10 min, data rate: low IoT, ZigBee
Waste Management (Smart City) Tolerable delay: 30 min, update frequency: LoRaWAN, SigFox, LTE, NB‑
1 hour, data rate: low IoT
Video Surveillance (Smart City) Tolerable delay: seconds, update frequency: LTE, NB‑IoT, WiFi
real‑time, data rate: high, netwaork coverage:
large/small
Air Quality Monitoring (Smart Tolerable delay: 5 min, update frequency: Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, NB‑IoT
Home) 30 min, data rate: low
Patients Healthcare Delivery and Tolerable delay: seconds, update frequency: Bluetooth, LTE, NB‑IoT
Monitoring (Healthcare) 1 report per hour/day, data rate: high
security: high, reliability: high
Real‑time Emergency Response Tolerable delay: seconds, update frequency: Bluetooth, LTE, NB‑IoT
and Remote Diagnostics (Health‑ ad‑hoc emergency communication, data rate:
care) high security: high, reliability: high
Smart Grids (Industrial) Tolerable delay: 3 to 20 ms, update frequency: WiFi, ZigBee, LTE, WiMAX,
10 to 100 ms, reliability: 10 −6 PLR, network cov‑ NB‑IoT
erage: a few meter to kilometers
Road Safety Highway (Smart City) Tolerable delay: 10 to 100 ms, update fre‑ LTE, NB‑IoT
quency: 100 ms, reliability: 10 −3 to 10 −5 PLR,
network coverage: 2000 m
Factory Automation (Industrial) Tolerable delay: 0.25 to 10 ms, update fre‑ LTE, NB‑IoT, WiFi
quency: 0.5 to 50 ms, reliability: 10 −9 PLR, net‑
work coverage: 50 to 100 m
Manufacturing Cell (Industrial) Tolerable delay: 5 ms, update frequency: 50 ms, LTE, NB‑IoT, WiFi
reliability: 10 −9 PLR, network coverage: 50 to
100 m
Process Automation (Industrial) Tolerable delay: 50 to 100 ms, update fre‑ LTE, NB‑IoT
quency: 100 to 5000 ms, reliability: 10 −3 to 10 −4
PLR, network coverage: 100 to 500 m
coverage range. High user mobility and extended bat‑ of IoE through the analysis and application of big data.
tery life of mobile terminals can be achieved using LTE. Also, IoE has the prospect of on‑time medical assistance
WiMAX supports broadband applications as well as pro‑ by connecting the network to traf ic and hospital adminis‑
viding large coverage, and deployment of a WiMAX net‑ tration in case of an accident. Moreover, IoE also supports
work is much cheaper than the deployment of an LTE net‑ the electronic reporting of patients’ mobility (i.e. contact
work for last‑mile connectivity. Cognitive radio technolo‑ tracing) to ensure homecare. IoE‑coupled smart wear‑
gies can achieve large coverage with non‑LoS links in last‑ able devices/systems have been reported for monitoring
mile connectivity in rural areas utilizing unused licensed cardiovascular disease, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
spectrum. Disease (COPD), Parkinson’s disease, pregnancy and cog‑
nitive disorder. Usually, the acquired data (biomarkers
The application of IoE promises smart, innovative and such as ECG, respiratory rate, body temperature, EMG
comfortable medical services to the patients and/or in‑ muscle activity, gait and others) using sensory devices are
dividuals needing healthcare, and furnishes their class transmitted to the Healthcare Organization (HCO) using
of life through easing emergency medical support, secu‑ the intermediate concentrators and platforms connected
rity and continuous care [57]. The prospective applica‑ with short‑range radio such as Zigbee or low‑power Blue‑
tions of IoE in medical sectors include health monitoring tooth under the governance of a smartphone’s WiFi or cel‑
using wearable devices that measure the physical activ‑ lular data connection [60].
ities/behaviour [58], supporting health‑related informa‑
tion for regular patient care, and networking through de‑ Some IoE applications, typical requirements and possible
vices for clinical care with issues of an unvarying electro‑ technologies are shown in Table 3. Wearables and smart
cardiogram, blood oxygen and blood pressure [59]. IoE metering are two potential IoE application areas. The net‑
can lead to constructing big data on a particular health working technologies used in these technologies are dis‑
issue and can play a pivotal role in the further progress cussed in the following subsections.
22 © International Telecommunication Union, 2021