Page 44 - ITU KALEIDOSCOPE, ATLANTA 2019
P. 44
2019 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
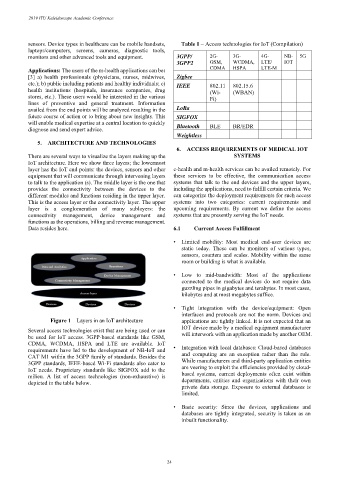
sensors. Device types in healthcare can be mobile handsets, Table 1 – Access technologies for IoT (Compilation)
laptops/computers, screens, cameras, diagnostic tools,
monitors and other advanced tools and equipment. 3GPP/ 2G- 3G- 4G- NB- 5G
3GPP2 GSM, WCDMA, LTE/ IOT
Applications: The users of the m-health applications can be: CDMA HSPA LTE-M
[3] a) health professionals (physicians, nurses, midwives, Zigbee
etc.); b) public including patients and healthy individuals; c) IEEE 802.11 802.15.6
health institutions (hospitals, insurance companies, drug (Wi- (WBAN)
stores, etc.). These users would be interested in the various Fi)
lines of preventive and general treatment. Information
availed from the end points will be analyzed resulting in the LoRa
future course of action or to bring about new insights. This SIGFOX
will enable medical expertise at a central location to quickly
diagnose and send expert advice. Bluetooth BLE BR/EDR
Weightless
5. ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGIES
6. ACCESS REQUIREMENTS OF MEDICAL IOT
There are several ways to visualize the layers making up the SYSTEMS
IoT architecture. Here we show three layers; the lowermost
layer has the IoT end points: the devices, sensors and other e-health and m-health services can be availed remotely. For
equipment that will communicate through intervening layers these services to be effective, the communication access
to talk to the application (s). The middle layer is the one that systems that talk to the end devices and the upper layers,
provides the connectivity between the devices to the including the applications, need to fulfill certain criteria. We
different modules and functions residing in the upper layer. can categorize the deployment requirements for such access
This is the access layer or the connectivity layer. The upper systems into two categories: current requirements and
layer is a conglomeration of many sublayers: the upcoming requirements. By current we define the access
connectivity management, device management and systems that are presently serving the IoT needs.
functions as the operations, billing and revenue management.
Data resides here. 6.1 Current Access Fulfillment
• Limited mobility: Most medical end-user devices are
static today. These can be monitors of various types,
sensors, counters and scales. Mobility within the same
room or building is what is available.
• Low to mid-bandwidth: Most of the applications
connected to the medical devices do not require data
guzzling pipes in gigabytes and terabytes. In most cases,
kilobytes and at most megabytes suffice.
• Tight integration with the device/equipment: Open
interfaces and protocols are not the norm. Devices and
Figure 1 – Layers in an IoT architecture applications are tightly linked. It is not expected that an
Several access technologies exist that are being used or can IOT device made by a medical equipment manufacturer
be used for IoT access. 3GPP-based standards like GSM, will interwork with an application made by another OEM.
CDMA, WCDMA, HSPA and LTE are available. IoT
requirements have led to the development of NB-IoT and • Integration with local databases: Cloud-based databases
CAT M1 within the 3GPP family of standards. Besides the and computing are an exception rather than the rule.
3GPP standards, IEEE-based Wi-Fi standards also cater to While manufacturers and third-party application entities
IoT needs. Proprietary standards like SIGFOX add to the are veering to exploit the efficiencies provided by cloud-
milieu. A list of access technologies (non-exhaustive) is based systems, current deployments often exist within
depicted in the table below. departments, entities and organizations with their own
private data storage. Exposure to external databases is
limited.
• Basic security: Since the devices, applications and
databases are tightly integrated, security is taken as an
inbuilt functionality.
– 24 –