Page 48 - ITU KALEIDOSCOPE, ATLANTA 2019
P. 48
2019 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
existing LTE radios. Architectural improvements like the
separation of Control and User planes (CUPs) in the core
layer and slicing where different user types can be allotted
their own virtual network helps in improving the latency that
is so critical in some use cases. These and further
enhancements bring more impetus to the deployment of IoT
systems, spectrum efficiency, higher bit rates, reduced
latency, connection density (devices/square Km) and
enhanced battery life of the devices [14] [15]. In further
updates through releases, 3GPP through NB-IoT, LTE and
5G is set to meet the needs for both massive Machine-Type
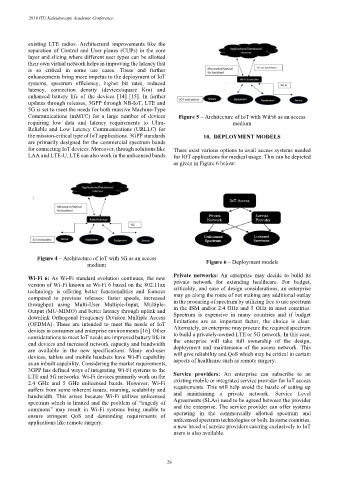
Communications (mMTC) for a large number of devices Figure 5 – Architecture of IoT with WiFi6 as an access
requiring low data and latency requirements to Ultra- medium
Reliable and Low Latency Communications (URLLC) for
the mission-critical type of IoT applications. 3GPP standards 10. DEPLOYMENT MODELS
are primarily designed for the commercial spectrum bands
for connecting IoT devices. Moreover, through solutions like There exist various options to avail access systems needed
LAA and LTE-U, LTE can also work in the unlicensed bands. for IOT applications for medical usage. This can be depicted
as given in Figure 6 below:
Figure 4 – Architecture of IoT with 5G as an access
medium Figure 6 – Deployment models
Wi-Fi 6: As Wi-Fi standard evolution continues, the new Private networks: An enterprise may decide to build its
version of Wi-Fi known as Wi-Fi 6 based on the 802.11ax private network for extending healthcare. For budget,
technology is offering better functionalities and features criticality, and ease of design considerations, an enterprise
compared to previous releases: faster speeds, increased may go along the route of not making any additional outlay
throughput using Multi-User Multiple-Input, Multiple- in the procuring of spectrum by utilizing free to use spectrum
Output (MU-MIMO) and better latency through uplink and in the ISM and/or 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz in most countries.
downlink Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access Spectrum is expensive in many countries and if budget
(OFDMA). These are intended to meet the needs of IoT limitations are an important factor, the choice is clear.
devices in consumer and enterprise environments [16]. Other Alternately, an enterprise may procure the required spectrum
considerations to meet IoT needs are improved battery life in to build a privately-owned LTE or 5G network. In this case,
end devices and increased network capacity and bandwidth the enterprise will take full ownership of the design,
are available in the new specifications. Many end-user deployment and maintenance of the access network. This
devices, tablets and mobile handsets have Wi-Fi capability will give reliability and QoS which may be critical in certain
as an inbuilt capability. Considering the market requirements, aspects of healthcare such as remote surgery.
3GPP has defined ways of integrating Wi-Fi systems to the
LTE and 5G networks. Wi-Fi devices primarily work on the Service providers: An enterprise can subscribe to an
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz unlicensed bands. However, Wi-Fi existing mobile or integrated service provider for IoT access
suffers from some inherent issues, roaming, scalability and requirements. This will help avoid the hassle of setting up
bandwidth. This arises because Wi-Fi utilizes unlicensed and maintaining a private network. Service Level
spectrum which is limited and the problem of “tragedy of Agreements (SLAs) need to be agreed between the provider
commons” may result in Wi-Fi systems being unable to and the enterprise. The service provider can offer systems
ensure stringent QoS and demanding requirements of operating in the commercially allotted spectrum and
applications like remote surgery. unlicensed spectrum technologies or both. In some countries,
a new breed of service providers catering exclusively to IoT
users is also available.
– 28 –