Page 799 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 799
Transport aspects 2
for the next (q+1)-th sync symbol position, after which the following z-1 VFRBs shall be reported every q-th
sync symbol position, etc. until the next request to update VFRB control parameters.
With the rule defined above, the VFRB are sent on the sync symbol positions associated with the
superframe count values CNTSF computed with the following recursive rule starting from n=0:
n
CNTSF = CNTSF if n = 0
0
n
16
CNTSF = (CNTSF n-1 + q) MOD 2 if n MOD z ≠ 0
n
16
CNTSF = (CNTSF n-1 + q + 1) MOD 2 if n MOD z = 0
n
where CNTSF is the superframe count value of the first sent VFRB.
0
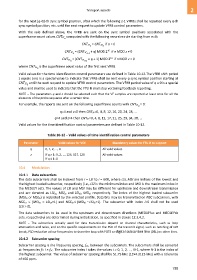
Valid values for the time identification control parameters are defined in Table 10-12.The VFRB shift period
z equals zero is a special value to indicate that VFRB shall be sent every q sync symbol position starting at
CNTSF until the next request to update VFRB control parameters. The VFRB period value of q = 0 is a special
0
value and shall be used to indicate that the FTU-R shall stop vectoring feedback reporting.
NOTE – The parameters q and z should be selected such that the VF samples are reported at least once for all the
elements of the probe sequence after a certain time.
For example, the reports are sent on the following superframe counts with CNTSF = 0:
0
q=4 and z=0 then CNTSF=0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, …
q=4 and z=4 then CNTSF=0, 4, 8, 12, 17, 21, 25, 29, 34, 38, …
Valid values for the time identification control parameters are defined in Table 10-12.
Table 10-12 – Valid values of time identification control parameters
Parameter Valid values for VCE Mandatory values for FTU-R to support
q 0, 1, 2, …, 8 All valid values.
z If q > 1: 0, 2, …, 126, 127, 128 All valid values.
If q ≤ 1: 0
10.4 Modulation
10.4.1 Data subcarriers
The data subcarriers shall be indexed from i = LSI to i = MSI, where LSI, MSI are indices of the lowest and
the highest loaded subcarrier, respectively (i.e., LSI is the minimum index and MSI is the maximum index in
the MEDLEY set). The values of LSI and MSI may be different for upstream and downstream transmission
and are denoted as LSIus, MSIus and LSIds, MSIds respectively. The index of the highest loaded subcarrier
(MSIus or MSIds) is restricted by the selected profile. Data bits may be transmitted on NSC subcarriers, with
NSCus (MSIus – LSIus+1) and NSCds (MSIds − LSIds+1). The subcarrier with index i=0 shall not be used
(LSI > 0).
The data subcarriers to be used in the upstream and downstream directions (MEDLEYus and MEDLEYds
sets, respectively) are determined during initialization, as specified in clause 12.3.4.2.
NOTE – The subcarriers actually used for data transmission depend on channel characteristics, such as loop
attenuation and noise, and on the specific requirements on the PSD of the transmit signal, such as notching of IAR
bands, PSD reduction at low frequencies to share the loop with POTS or digital subscriber line (DSL) on other lines.
10.4.2 Subcarrier spacing
Subcarrier spacing is the frequency spacing, fSC, between the subcarriers. The subcarriers shall be centered
at frequencies f= i × fSC. The subcarrier index i takes the values i = 0, 1, 2, ..., N-1, where N-1 is the index of
the highest subcarrier. The value of subcarrier spacing shall be 51.75 kHz (12×4.3125 kHz) with a tolerance
of 50 ppm.
789