Page 29 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2024
P. 29
Parameter Value
SCS 120 KHz
No. of Tx antennas 1
No. of Rx antennas 1
No. of PRBs 198
No. of subcarriers 12
per PRB
Bandwidth 120
expansion (2v)
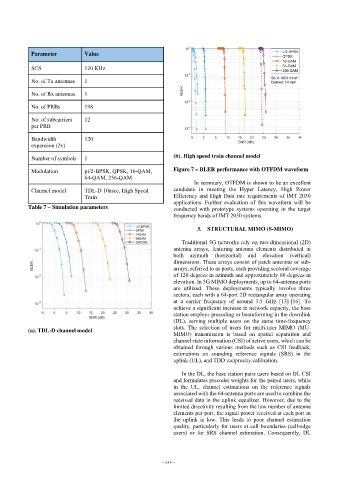
Number of symbols 1 (b). High speed train channel model
Modulation pi/2-BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, Figure 7 – BLER performance with OTFDM waveform
64-QAM, 256-QAM
In summary, OTFDM is shown to be an excellent
Channel model TDL-D 10nsec, High Speed candidate in meeting the Hyper Latency, High Power
Train Efficiency and High Data rate requirements of IMT 2030
applications. Further evaluation of this waveform will be
Table 7 – Simulation parameters conducted with prototype systems operating in the target
frequency bands of IMT 2030 systems.
3. STRUCTURAL MIMO (S-MIMO)
Traditional 5G networks rely on two-dimensional (2D)
antenna arrays, featuring antenna elements distributed in
both azimuth (horizontal) and elevation (vertical)
dimensions. These arrays consist of patch antennas or sub-
arrays, referred to as ports, each providing sectoral coverage
of 120 degrees in azimuth and approximately 60 degrees in
elevation. In 5G MIMO deployments, up to 64-antenna ports
are utilized. These deployments typically involve three
sectors, each with a 64-port 2D rectangular array operating
at a carrier frequency of around 3.5 GHz [13]-[16]. To
achieve a significant increase in network capacity, the base
station employs precoding or beamforming in the downlink
(DL), serving multiple users on the same time-frequency
(a). TDL-D channel model slots. The selection of users for multi-user MIMO (MU-
MIMO) transmission is based on spatial separation and
channel state information (CSI) of active users, which can be
obtained through various methods such as CSI feedback,
estimations on sounding reference signals (SRS) in the
uplink (UL), and TDD reciprocity calibration.
In the DL, the base station pairs users based on DL CSI
and formulates precoder weights for the paired users, while
in the UL, channel estimations on the reference signals
associated with the 64-antenna ports are used to combine the
received data in the uplink equalizer. However, due to the
limited directivity resulting from the low number of antenna
elements per port, the signal power received at each port in
the uplink is low. This leads to poor channel estimation
quality, particularly for users at cell boundaries (cell-edge
users) or for SRS channel estimation. Consequently, DL
– xxv –