Page 99 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2020
P. 99
Industry-driven digital transformation
E-UTRA
E-UTRA & NR
E-UTRA & NR
Hotspot Path 1 E-UTRA E-UTRA & NR 5G deployment paths in Hotspots Path 1 E-UTRA E-UTRA & NR E-UTRA & NR
E-UTRA & NR
E-UTRA & NR
E-UTRA
Path 2
Path 2
Urban Path 1 E-UTRA E-UTRA & NR E-UTRA & NR Dense Urban Path 3 E-UTRA E-UTRA & NR E-UTRA & NR
5G deployment path in Urban areas
Path 4 E-UTRA E-UTRA
Centralized deployment of 5G in rural
Rural Path 1 E-UTRA E-UTRA & NR areas is not advisable due to low traffic 5G deployment paths in Dense
and low return on investment.
Distributed 4G RAN 5G deployment path in Rural areas Path 5 E-UTRA E-UTRA Urban areas
Common for most operators
Note 1: Depending on traffic/location, there are different 5G deployment choices (hotspots, dense urban areas, urban areas, and rural areas)
Note 2: In practice, choosing a 5G deployment plan depends on the availability of capital, service affordability, expected traffic, locations of existing eNB sites, and availability of spectrum
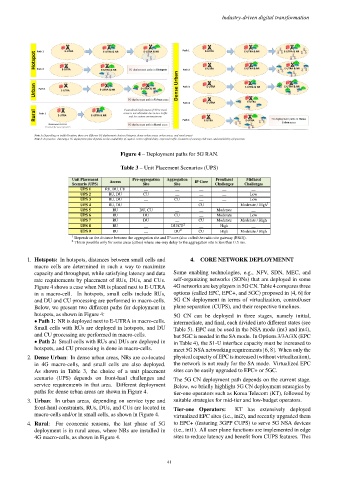
Figure 4 – Deployment paths for 5G RAN.
Table 3 – Unit Placement Scenarios (UPS)
Unit Placement Access Pre-aggregation Aggregation IP Core Fronthaul Midhaul
Scenario (UPS) Site Site Challenges Challenges
UPS 1 RU, DU, CU __ __ __ __ __
UPS 2 RU, DU CU __ __ __ Low
UPS 3 RU, DU __ CU __ __ Low
UPS 4 RU, DU __ __ CU __ Moderate / High 1
UPS 5 RU DU, CU __ __ Moderate __
UPS 6 RU DU CU __ Moderate Low
UPS 7 RU DU __ CU Moderate Moderate / High
UPS 8 RU __ DU/CU 2 __ High __
UPS 9 RU __ DU 2 CU High Moderate / High
1 Depends on the distance between the aggregation site and IP core (also called the radio site gateway (RSG)).
2 This is possible only for some areas (cities) where one-way delay to the aggregation site is less than 0.5 ms.
1. Hotspots: In hotspots, distances between small cells and 4. CORE NETWORK DEPLOYMENNT
macro cells are determined in such a way to maximize
capacity and throughput, while satisfying latency and data Some enabling technologies, e.g., NFV, SDN, MEC, and
rate requirements by placement of RUs, DUs, and CUs. self-organizing networks (SONs) that are deployed in some
Figure 4 shows a case when NR is placed next to E-UTRA 4G networks are key players in 5G CN. Table 4 compares three
in a macro-cell. In hotspots, small cells include RUs, options (called EPC, EPC+, and 5GC) proposed in [4, 6] for
and DU and CU processing are performed in macro-cells. 5G CN deployment in terms of virtualization, control/user
Below, we present two different paths for deployment in plane separation (CUPS), and their respective timelines.
hotspots, as shown in Figure 4: 5G CN can be deployed in three stages, namely initial,
• Path 1: NR is deployed next to E-UTRA in macro-cells. intermediate, and final, each divided into different states (see
Small cells with RUs are deployed in hotspots, and DU Table 5). EPC can be used in the NSA mode (int3 and int4),
and CU processing are performed in macro-cells. but 5GC is needed in the SA mode. In Options 3/3A/3X (EPC
• Path 2: Small cells with RUs and DUs are deployed in in Table 4), the S1-U interface capacity must be increased to
hotspots, and CU processing is done in macro-cells. meet 5G NSA networking requirements [6, 8]. When only the
2. Dense Urban: In dense urban areas, NRs are co-located physical capacity of EPC is increased (without virtualization),
in 4G macro-cells, and small cells are also deployed. the network is not ready for the SA mode. Virtualized EPC
As shown in Table 3, the choice of a unit placement sites can be easily upgraded to EPC+ or 5GC.
scenario (UPS) depends on front-haul challenges and The 5G CN deployment path depends on the current stage.
service requirements in that area. Different deployment Below, we briefly highlight 5G CN deployment strategies by
paths for dense urban areas are shown in Figure 4. tier-one operators such as Korea Telecom (KT), followed by
3. Urban: In urban areas, depending on service type and suitable strategies for mid-tier and low-budget operators.
front-haul constraints, RUs, DUs, and CUs are located in Tier-one Operators: KT has extensively deployed
macro-cells and/or in small cells, as shown in Figure 4. virtualized EPC sites (i.e., ini2), and recently upgraded them
4. Rural: For economic reasons, the last phase of 5G to EPC+ (featuring 3GPP CUPS) to serve 5G NSA devices
deployment is in rural areas, where NRs are installed in (i.e., int1). All user plane functions are implemented in edge
4G macro-cells, as shown in Figure 4. sites to reduce latency and benefit from CUPS features. This
– 41 –