Page 110 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2020
P. 110
2020 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
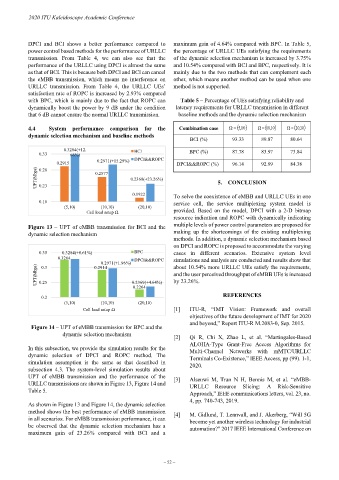
DPCI and BCI shows a better performance compared to maximum gain of 4.64% compared with BPC. In Table 5,
power control based methods for the performance of URLLC the percentage of URLLC UEs satisfying the requirements
transmission. From Table 4, we can also see that the of the dynamic selection mechanism is increased by 3.75%
performance of the URLLC using DPCI is almost the same and 10.54% compared with BCI and BPC, respectively. It is
as that of BCI. This is because both DPCI and BCI can cancel mainly due to the two methods that can complement each
the eMBB transmission, which means no interference on other, which means another method can be used when one
URLLC transmission. From Table 4, the URLLC UEs’ method is not supported.
satisfaction rate of ROPC is increased by 2.93% compared
with BPC, which is mainly due to the fact that ROPC can Table 5 – Percentage of UEs satisfying reliability and
dynamically boost the power by 9 dB under the condition latency requirements for URLLC transmission in different
that 6 dB cannot ensure the normal URLLC transmission. baseline methods and the dynamic selection mechanism
10
, 5
4.4 System performance comparison for the Combination case Ω = ( ) Ω = ( 10,10 ) Ω = ( 10,20 )
dynamic selection mechanism and baseline methods
BCI (%) 93.33 89.87 80.64
0.3284(+12. BCI BPC (%) 87.78 83.97 73.84
0.33 66%)
0.2915 0.2971(+15.29%) DPCI&&ROPC DPCI&&ROPC (%) 96.14 92.99 84.38
0.28
UPT(Mbps) 0.23 0.2577 0.2369(+23.26%) 5. CONCLUSION
0.1922 To solve the coexistence of eMBB and URLLC UEs in one
0.18 service cell, the service multiplexing system model is
(5,10) (10,10) (20,10)
Cell load setup Ω provided. Based on the model, DPCI with a 2-D bitmap
resource indication and ROPC with dynamically indicating
Figure 13 – UPT of eMBB transmission for BCI and the multiple levels of power control parameters are proposed for
dynamic selection mechanism making up the shortcomings of the existing multiplexing
methods. In addition, a dynamic selection mechanism based
on DPCI and ROPC is proposed to accommodate the varying
0.35 0.3284(+0.61%) BPC cases in different scenarios. Extensive system level
0.3264 DPCI&&ROPC simulations and analysis are conducted and results show that
0.2971(+1.96%) about 10.54% more URLLC UEs satisfy the requirements,
UPT(Mbps) and the user perceived throughput of eMBB UEs is increased
0.2914
0.3
by 23.26%.
0.2369(+4.64%)
0.25
0.2264
REFERENCES
0.2
(5,10) (10,10) (20,10)
Cell load setup Ω [1] ITU-R, “IMT Vision: Framework and overall
objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020
and beyond,” Report ITU-R M.2083-0, Sep. 2015.
Figure 14 – UPT of eMBB transmission for BPC and the
dynamic selection mechanism [2] Qi R, Chi X, Zhao L, et al. “Martingales-Based
ALOHA-Type Grant-Free Access Algorithms for
In this subsection, we provide the simulation results for the Multi-Channel Networks with mMTC/URLLC
dynamic selection of DPCI and ROPC method. The Terminals Co-Existence,” IEEE Access, pp (99). 1-1,
simulation assumption is the same as that described in 2020.
subsection 4.3. The system-level simulation results about
UPT of eMBB transmission and the performance of the [3] Alsenwi M, Tran N H, Bennis M, et al. “eMBB-
URLLC transmissions are shown in Figure 13, Figure 14 and URLLC Resource Slicing: A Risk-Sensitive
Table 5. Approach,” IEEE communications letters, vol. 23, no.
4, pp. 740-743, 2019.
As shown in Figure 13 and Figure 14, the dynamic selection
method shows the best performance of eMBB transmission [4] M. Gidlund, T. Lennvall, and J. Akerberg, “Will 5G
in all scenarios. For eMBB transmission performance, it can become yet another wireless technology for industrial
be observed that the dynamic selection mechanism has a automation?” 2017 IEEE International Conference on
maximum gain of 23.26% compared with BCI and a
– 52 –