Page 36 - Digital Financial Services security assurance framework
P. 36
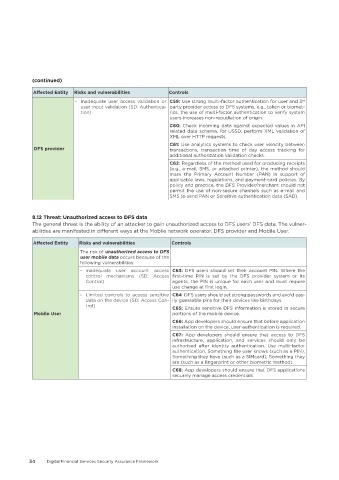
(continued)
Affected Entity Risks and vulnerabilities Controls
- Inadequate user access validation or C59: Use strong multi-factor authentication for user and 3
rd
user input validation (SD: Authentica- party provider access to DFS systems, e.g., token or biomet-
tion) rics, the use of multi-factor authentication to verify system
users increases non-repudiation of origin.
C60: Check incoming data against expected values in API
related data schema, for USSD, perform XML validation of
XML over HTTP requests.
C61: Use analytics systems to check user velocity between
DFS provider transactions, transaction time of day access tracking for
additional authorization validation checks.
C62: Regardless of the method used for producing receipts
(e.g., e-mail, SMS, or attached printer), the method should
mask the Primary Account Number (PAN) in support of
applicable laws, regulations, and payment-card policies. By
policy and practice, the DFS Provider/merchant should not
permit the use of non-secure channels such as e-mail and
SMS to send PAN or Sensitive authentication data (SAD).
8�12 Threat: Unauthorized access to DFS data
The general threat is the ability of an attacker to gain unauthorized access to DFS users' DFS data. The vulner-
abilities are manifested in different ways at the Mobile network operator, DFS provider and Mobile User.
Affected Entity Risks and vulnerabilities Controls
The risk of unauthorized access to DFS
user mobile data occurs because of the
following vulnerabilities:
- Inadequate user account access C63: DFS users should set their account PIN. Where the
control mechanisms (SD: Access first-time PIN is set by the DFS provider system or its
Control) agents, the PIN is unique for each user and must require
use change at first login.
- Limited controls to access sensitive C64: DFS users should set strong passwords and avoid eas-
data on the device (SD: Access Con- ily guessable pins for their devices like birthdays.
trol) C65: Ensure sensitive DFS information is stored in secure
Mobile User portions of the mobile device.
C66: App developers should ensure that before application
installation on the device, user authentication is required.
C67: App developers should ensure that access to DFS
infrastructure, application, and services should only be
authorised after identity authentication. Use multi-factor
authentication, Something the user knows (such as a PIN),
Something they have (such as a SIMcard), Something they
are (such as a fingerprint or other biometric method).
C68: App developers should ensure that DFS applications
securely manage access credentials.
34 Digital Financial Services Security Assurance Framework