Page 39 - Digital Financial Services security assurance framework
P. 39
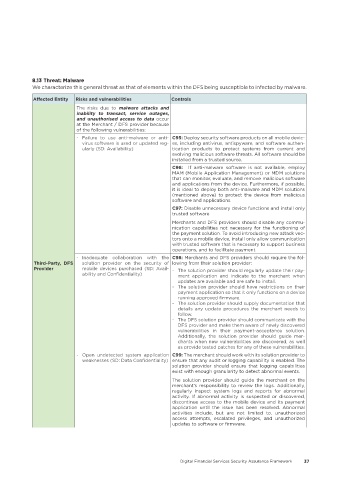
8�13 Threat: Malware
We characterize this general threat as that of elements within the DFS being susceptible to infected by malware.
Affected Entity Risks and vulnerabilities Controls
The risks due to malware attacks and
inability to transact, service outages,
and unauthorised access to data occur
at the Merchant / DFS provider because
of the following vulnerabilities:
- Failure to use anti-malware or anti- C95: Deploy security software products on all mobile devic-
virus software is used or updated reg- es, including antivirus, antispyware, and software authen-
ularly (SD: Availability) tication products to protect systems from current and
evolving malicious software threats. All software should be
installed from a trusted source.
C96: If anti-malware software is not available, employ
MAM (Mobile Application Management) or MDM solutions
that can monitor, evaluate, and remove malicious software
and applications from the device. Furthermore, if possible,
it is ideal to deploy both anti-malware and MDM solutions
(mentioned above) to protect the device from malicious
software and applications.
C97: Disable unnecessary device functions and install only
trusted software
Merchants and DFS providers should disable any commu-
nication capabilities not necessary for the functioning of
the payment solution. To avoid introducing new attack vec-
tors onto a mobile device, install only allow communication
with trusted software that is necessary to support business
operations, and to facilitate payment.
- Inadequate collaboration with the C98: Merchants and DFS providers should require the fol-
Third-Party, DFS solution provider on the security of lowing from their solution provider:
Provider mobile devices purchased (SD: Avail- - The solution provider should regularly update their pay-
ability and Confidentiality) ment application and indicate to the merchant when
updates are available and are safe to install.
- The solution provider should have restrictions on their
payment application so that it only functions on a device
running approved firmware.
- The solution provider should supply documentation that
details any update procedures the merchant needs to
follow.
- The DFS solution provider should communicate with the
DFS provider and make them aware of newly discovered
vulnerabilities in their payment-acceptance solution.
Additionally, the solution provider should guide mer-
chants when new vulnerabilities are discovered, as well
as provide tested patches for any of these vulnerabilities.
- Open undetected system application C99: The merchant should work with its solution provider to
weaknesses (SD: Data Confidentiality) ensure that any audit or logging capability is enabled. The
solution provider should ensure that logging capabilities
exist with enough granularity to detect abnormal events.
The solution provider should guide the merchant on the
merchant’s responsibility to review the logs. Additionally,
regularly inspect system logs and reports for abnormal
activity. If abnormal activity is suspected or discovered,
discontinue access to the mobile device and its payment
application until the issue has been resolved. Abnormal
activities include, but are not limited to, unauthorized
access attempts, escalated privileges, and unauthorized
updates to software or firmware.
Digital Financial Services Security Assurance Framework 37