Page 272 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 272
4 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
5.2 Application to IMT-2020
Many ICN gaps were identified in the FG IMT-2020 Phase-1 study (ITU 2015). This POC addresses the following
gaps and illustrates corresponding advantages:
1) Gap E.1 Considering ICN as a protocol for IMT-2020
ICN/NDN transport provides the foundation for creating service chains of named functions (Sifalakis,
et al. 2014) and named content (identified in the Interest request).
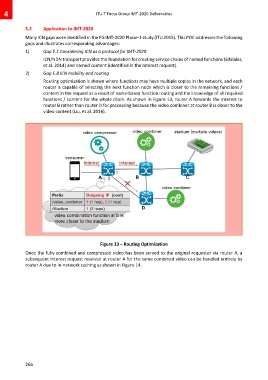
2) Gap E.8 ICN mobility and routing
Routing optimization is shown where functions may have multiple copies in the network, and each
router is capable of selecting the next function node which is closer to the remaining functions /
content in the request as a result of name-based function routing and the knowledge of all required
functions / content for the whole chain. As shown in Figure 13, router A forwards the Interest to
router B rather than router D for processing because the video combiner at router B is closer to the
video content (Liu, et al. 2016).
Figure 13 – Routing Optimization
Once the fully combined and compressed video has been served to the original requester via router A, a
subsequent Interest request received at router A for the same combined video can be handled entirely by
router A due to in-network caching as shown in Figure 14.
266