Page 270 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 270
4 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
4 ICN Enhanced Mobile Video at the Network Edge (Cisco)
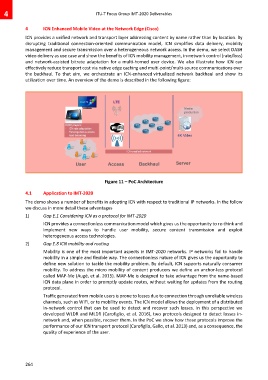
ICN provides a unified network and transport layer addressing content by name rather than by location. By
disrupting traditional connection-oriented communication model, ICN simplifies data delivery, mobility
management and secure transmission over a heterogeneous network access. In the demo, we select DASH
video delivery as use case and show the benefits of ICN mobility management, in-network control (rate/loss)
and network-assisted bitrate adaptation for a multi-homed user device. We also illustrate how ICN can
effectively reduce transport cost via native edge caching and multi-point/multi-source communications over
the backhaul. To that aim, we orchestrate an ICN-enhanced virtualized network backhaul and show its
utilization over time. An overview of the demo is described in the following figure:
Figure 11 – PoC Architecture
4.1 Application to IMT-2020
The demo shows a number of benefits in adopting ICN with respect to traditional IP networks. In the follow
we discuss in more detail these advantages
1) Gap E.1 Considering ICN as a protocol for IMT-2020
ICN provides a connectionless communication model which gives us the opportunity to re-think and
implement new ways to handle user mobility, secure content transmission and exploit
heterogeneous access technologies.
2) Gap E.8 ICN mobility and routing
Mobility is one of the most important aspects in IMT-2020 networks. IP networks fail to handle
mobility in a simple and flexible way. The connectionless nature of ICN gives us the opportunity to
define new solution to tackle the mobility problem. By default, ICN supports naturally consumer
mobility. To address the micro mobility of content producers we define an anchor-less protocol
called MAP-Me (Augé, et al. 2015). MAP-Me is designed to take advantage from the name-based
ICN data plane in order to promptly update routes, without waiting for updates from the routing
protocol.
Traffic generated from mobile users is prone to losses due to connection through unreliable wireless
channels, such as WIFI, or to mobility events. The ICN model allows the deployment of a distributed
in-network control that can be used to detect and recover such losses. In this perspective we
developed WLDR and MLDR (Carofiglio, et al. 2016), two protocols designed to detect losses in-
network and, when possible, recover them. In the PoC we show how these protocols improve the
performance of our ICN transport protocol (Carofiglio, Gallo, et al. 2013) and, as a consequence, the
quality of experience of the user.
264