Page 565 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 565
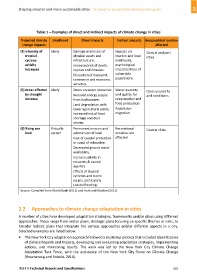
Table 1 – Examples of direct and indirect impacts of climate change in cities
Projected climate Likelihood Direct impacts Indirect impacts Geographical location
change impacts affected
(4) Intensity of Likely Damage and losses of Impacts on Coastal and port
tropical physical assets and tourism and local cities.
cyclone infrastructure. livelihoods,
activity Increased risk of death, psychological
increases injuries and illnesses. impacts/stress of
Disruption of transport, vulnerable
commerce and economic populations.
activities.
(5) Areas affected Likely Stress on water resources Water quantity Cities unused to
by drought Reduced energy supply and quality for arid conditions.
increase from hydropower. consumption and
Land degradation with food production
lower agricultural yields, Population
increased risk of food migration.
shortage and dust
storms.
(6) Rising sea Virtually Permanent erosion and Recreational Coastal cities.
level certain submersion of land. activities are
Cost of coastal protection affected.
or coast of relocation.
Decreased ground water
availability.
Increase salinity in
estuaries & coastal
aquifers.
Effects of tropical
cyclones and storm
surges, particularly
coastal flooding.
Source: Compiled from World Bank (2011) and Hunt and Watkiss (2011)
2.2 Approaches to climate change adaptation in cities
A number of cities have developed adaptation strategies, frameworks and/or plans using different
approaches. These range from sector plans, strategic plans focusing on specific themes or risks, to
broader holistic plans that integrate the various approaches and/or different aspects in a city.
Selected examples are listed below:
The New York City adaptation approach followed a multistep process that included identification
of climate hazards and impacts, developing and evaluating adaptation strategies, implementing
actions, and monitoring results. The work was led by the New York City Climate Change
Adaptation Task Force, with the assistance of the New York City Panel on Climate Change
(Rosenzweig and Solecki, 2010).
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 555