Page 570 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 570
development of standards for disaster relief systems and to advance the work the recovery and
resilience of network infrastructure.
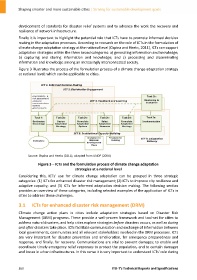
Finally it is important to highlight the potential role that ICTs have to promote informed decision
making in the adaptation processes. According to research on the role of ICTs in the formulation of
climate change adaptation strategy at the national level (Ospina and Heeks, 2011), ICTs can support
adaptation strategies within the three broad categories: a) generating information and knowledge;
b) capturing and storing information and knowledge; and c) processing and disseminating
information and knowledge among an increasingly interconnected society.
Figure 3 illustrates the process of the formulation process of a climate change adaptation strategy
at national level; which can be applicable to cities.
Source: Ospina and Heeks (2011), adapted from UNDP (2004)
Figure 3 – ICTs and the formulation process of climate change adaptation
strategies at a national level
Considering this, ICTs' use for climate change adaptation can be grouped in three strategic
categories: (1) ICTs for enhanced disaster risk management; (2) ICTs to improve city resilience and
adaptive capacity; and (3) ICTs for informed adaptation decision making. The following section
provides an overview of these categories, including selected examples of the application of ICTs in
cities to address these challenges.
3.1 ICTs for enhanced disaster risk management (DRM)
Climate change action plans in cities include adaptation strategies based on Disaster Risk
Management (DRM) programs. These provide a well‐proven framework and tool‐set for cities to
address natural disasters, and help cities explore strategies before disasters occurs, as well as during
and after disasters take place. ICTs facilitate communication and exchange of information between
local governments, communities and all relevant stakeholders involved in the DRM processes. ICTs
are very important for disaster prevention and amelioration, for emergency preparedness and
response, and finally, for recovery. Communications are vital to prevent damages; to enable and
coordinate timely emergency relief responses to protect the population, and to contain damages
and losses in urban infrastructures. In this sense it is very important to understand ICTs' role during
560 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications