Page 209 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 209
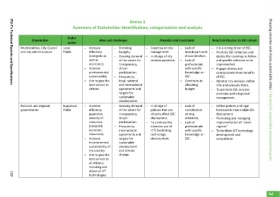
Role/contribution to SSC rollout It is a strong driver of SSC. Promote SSC initiatives and decide the roadmap to follow and specific solutions to be implemented. Engage citizens and communicate them benefits of SSC. Monitor city services: define KPIs and evaluate them. To promote SSC services provision and integrated management. Define policies and legal frameworks that enable SSC deployment. Promoting and managing implem
–
interdepartment – al coordination. Lack of professionals with specific – knowledge on SSC. Constrains in – allocating budget. – – Lack of coordination among ministries. – Lack of professionals with specific – knowledge on SSC.
Potential and constraints – Expertise on city – services provision. – – directly affect SSC –
Lack of
– management. In charge of city – In charge of – policies that can deployment. To promote the – intensive use of ICTs facilitating technology development.
Annex 1 Summary of Stakeholder Identification, categorization and analysis Growing demand of the voters for transparency, participation. Pressure by local, national and international agreements and targets for sustainable development. Growing demand of the voters for transparency, participation. Pressure by international agreements and targets for sustainable development and climate
Aims and challenges Shrinking – budgets. – citizen – – citizen – change.
Increase efficiency (energetic as well as economic). Increase environmental sustainability. Aim to give the best service to citizens. Increase efficiency guarantee security of resources. (natural & economic resources). Increase environmental sustainability of the country. Aim to give the best service to all citizens; including and above all ICT technologies.
– – – – – –
Scale/ sector Supralocal
Local Public Public
Municipalities, City Council and city administration National and regional governments
Stakeholder
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 199