Page 444 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2024
P. 444
2024 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
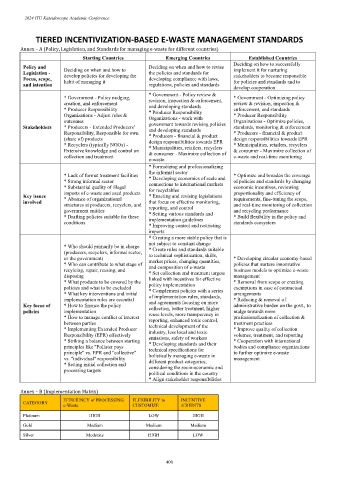
TIERED INCENTIVIZATION-BASED E-WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS
Annex – A (Policy, Legislation, and Standards for managing e-waste for different countries)
Starting Countries Emerging Countries Established Countries
Deciding on how to successfully
Policy and Deciding on when and how to Deciding on when and how to revise implement it for nurturing
Legislation - develop policies for developing the the policies and standards for stakeholders to become responsible
Focus, scope, habit of managing it developing compliance with laws, for policies and standards and to
and intention regulations, policies and standards develop cooperation
* Government - Policy review &
* Government - Policy nudging, revision, inspection & enforcement, * Government - Optimizing policy
creation, and enforcement review & revision, inspection &
* Producer Responsibility and developing standards enforcement, and standards
* Producer Responsibility
Organizations - Adjust rules & Organizations - work with * Producer Responsibility
outcomes Organizations - Optimize policies,
Stakeholders * Producers - Extended Producers' government towards revising policies standards, monitoring & enforcement
and developing standards
Responsibility, Responsible for own * Producers - financial & product * Producers - financial & product
(share of) products design responsibilities towards EPR design responsibilities towards EPR
* Recyclers (typically NGOs) - * Municipalities, retailers, recyclers * Municipalities, retailers, recyclers
Extensive knowledge and control on & consumer - Maximize collection of & consumer - Maximize collection of
collection and treatment e-waste e-waste and real-time monitoring
* Formalizing and professionalizing
the informal sector
* Lack of format treatment facilities * Developing economies of scale and * Optimize and broaden the coverage
* Strong informal sector connections to international markets of policies and standards by changing
* Substantial quality of illegal for recyclables economic incentives, reviewing
imports of e-waste and used products proportionality and efficiency of
Key issues * Absence of organizational * Enacting and revising legislations requirements, fine-tuning the scope,
involved that focus on effective monitoring,
structures at producers, recyclers, and reporting, and control and real-time monitoring of collection
government entities * Setting various standards and and recycling performance
* Drafting policies suitable for these implementation guidelines * Build flexibility in the policy and
conditions standards ecosystem
* Improving control and restricting
imports
* Creating a more stable policy that is
not subject to constant change
* Who should primarily be in charge * Create rules and standards suitable
(producers, recyclers, informal sector, to technical sophistication, skills,
or the government) market prices, changing quantities, * Developing circular economy-based
* Who can contribute to what stage of and composition of e-waste policies that nurture innonvative
recylcing, repair, reusing, and * Set collection and treatment targets business models to optimize e-waste
disposing linked with incentives for effective management
* What products to be covered by the * Removal from scope or creating
policies and what to be excluded policy implementation exemptions in case of contractual
* Complement policies with a series
* What key interventions and initial of implementation rules, standards, arrangements
implementation rules are essential * Reducing & removal of
Key focus of * How to finance the policy and agreements focusing on more administrative burden on the govt., to
collection, better treatment, higher
policies implementation reuse levels, more transparency in nudge towards more
* How to manage conflict of interest professionalization of collection &
between parties reporting, enhanced toxic control, treatment practices
technical development of the
* Implementing Extended Producer industry, less local and toxic * Improve quality of collection
Responsibility (EPR) effectively emissions, safety of workers volumes, treatment, and reporting
* Striking a balance between starting * Developing standards and their * Cooperation with international
principles like "Polluter pays technical specifications for bodies and compliance organizations
principle" vs. EPR and "collective" holistically managing e-waste in to further optimize e-waste
vs. "individual" responsibility different product categories, management
* Setting initial collection and considering the socio-economic and
processing targets political conditions in the country
* Align stakeholder responsibilities
Annex – B (Implementation Matrix)
EFFICIENCY of PROCESSING FLEXIBILITY to INCENTIVE
CATEGORY
e-Waste CUSTOMIZE /CREDITS
Platinum HIGH LOW HIGH
Gold Medium Medium Medium
Silver Moderate HIGH LOW
– 400 –