Page 235 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2024
P. 235
Innovation and Digital Transformation for a Sustainable World
Table 2 – Details of Agricultural IoT Devices and Services hit by Shodan search
Product Country Purpose description Devices Hit (a)
Temperature,
Three types of agricultural IT sensors for paddy fields, fields,
Sensor A Japan Humidity, 2
and weather. Users can upload measurement data to the cloud.
Water level
Service for storing sensor data. Graph display and
Service A Korea Application 8
Excel file downloads are provided for the user.
A water level management system comprises a water level
water level
System A Japan sensor, supply gate, and cloud infrastructure. 1
control
It enables remote water management for paddy fields.
A smart remote control system comprises sensors, controllers,
Production
System B Korea and a cloud infrastructure. It enables the user 5
management
to monitor sensor data and view camera footage.
This cultivation management support system enables the user to
Production
System C United States observe changes in crop growth and uneven growth within fields 19
management
by acquiring imagery from satellites and analyzing it using AI.
(a) They are the same product type but are associated with different IP addresses.
results do not indicate large-scale infections in the agriculture
sector, and the current risk appears to be low. However, the
importance of security measures and monitoring in this area
remains high.
5. LIST OF POTENTIAL RISKS RELATED TO
AGRICULTURAL IOT DEVICES
5.1 Existing security reports
This section presents security threats related to smart
agriculture and agricultural IoT devices as detailed in reports
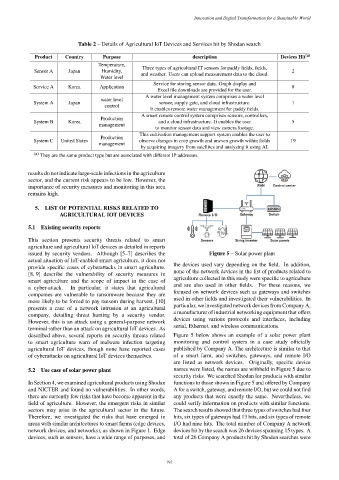
issued by security vendors. Although [5–7] describes the Figure 5 – Solar power plant
actual situation of IoT-enabled smart agriculture, it does not
the devices used vary depending on the field. In addition,
provide specific cases of cyberattacks in smart agriculture.
none of the network devices in the list of products related to
[8, 9] describe the vulnerability of security measures in
agriculture collected in this study were specific to agriculture
smart agriculture and the scope of impact in the case of
and are also used in other fields. For these reasons, we
a cyber-attack. In particular, it states that agricultural
focused on network devices such as gateways and switches
companies are vulnerable to ransomware because they are
used in other fields and investigated their vulnerabilities. In
more likely to be forced to pay ransom during harvest. [10]
particular, we investigated network devices from Company A,
presents a case of a network intrusion at an agricultural
a manufacturer of industrial networking equipment that offers
company, detailing threat hunting by a security vendor.
devices using various protocols and interfaces, including
However, this is an attack using a general-purpose network
serial, Ethernet, and wireless communications.
terminal rather than an attack on agricultural IoT devices. As
described above, several reports on security threats related Figure 5 below shows an example of a solar power plant
to smart agriculture warn of malware infection targeting monitoring and control system in a case study officially
agricultural IoT devices, though none have reported cases published by Company A. The architecture is similar to that
of cyberattacks on agricultural IoT devices themselves. of a smart farm, and switches, gateways, and remote I/O
are listed as network devices. Originally, specific device
5.2 Use case of solar power plant names were listed, the names are withheld in Figure 5 due to
security risks. We searched Shodan for products with similar
In Section 4, we examined agricultural products using Shodan functions to those shown in Figure 5 and offered by Company
and NICTER and found no vulnerabilities. In other words, A for a switch, gateway, and remote I/O, but we could not find
there are currently few risks that have become apparent in the any products that were exactly the same. Nevertheless, we
field of agriculture. However, the emergent risks in similar could verify information on products with similar functions.
sectors may arise in the agricultural sector in the future. The search results showed that three types of switches had four
Therefore, we investigated the risks that have emerged in hits, six types of gateways had 13 hits, and six types of remote
areas with similar architectures to smart farms (edge devices, I/O had nine hits. The total number of Company A network
network devices, and networks), as shown in Figure 1. Edge devices hit by the search was 26 devices spanning 15 types. A
devices, such as sensors, have a wide range of purposes, and total of 26 Company A products hit by Shodan searches were
– 191 –