Page 65 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3 – Internet of Bio-Nano Things for health applications
P. 65
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3
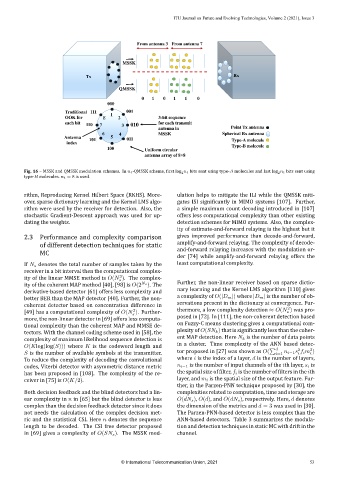
From antenna 3 From antenna 7
MSSK
Tx Rx
QMSSK
0 1 0 1 1 0
000
Traditional 111 1 001
OOK for 8 2 3-bit sequence
each bit 110 7 3 010 for each transmit
antenna in Point Tx antenna
6 4 MSSK Spherical Rx antenna
Antenna 101 5 011 Type-A molecule
index Type-B molecule
100 Uniform circular
antenna array of 8×8
Fig. 16 – MSSK and QMSSK modulation schemes. In n t‑QMSSK scheme, irst log n t bits sent using type‑A molecules and last log n t bits sent using
2
2
type‑B molecules. n t = 8 is used.
rithm, Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space (RKHS). More‑ ulation helps to mitigate the ILI while the QMSSK miti‑
over, sparse dictionary learning and the Kernel LMS algo‑ gates ISI signi icantly in MIMO systems [107]. Further,
rithm were used by the receiver for detection. Also, the a simple maximum count decoding introduced in [107]
stochastic Gradient‑Descent approach was used for up‑ offers less computational complexity than other existing
dating the weights. detection schemes for MIMO systems. Also, the complex‑
ity of estimate‑and‑forward relaying is the highest but it
2.3 Performance and complexity comparison gives improved performance than decode‑and‑forward,
of different detection techniques for static amplify‑and‑forward relaying. The complexity of decode‑
MC and‑forward relaying increases with the modulation or‑
der [74] while amplify‑and‑forward relaying offers the
If N s denotes the total number of samples taken by the least computational complexity.
receiver in a bit interval then the computational complex‑
3
ity of the linear MMSE method is O(N ). The complex‑
s
ity of the coherent MAP method [40], [98] is O(2 N s ). The Further, the non‑linear receiver based on sparse dictio‑
nary learning and the Kernel LMS algorithm [110] gives
derivative‑based detector [61] offers less complexity and
a complexity of O(|D m |) where |D m | is the number of ob‑
better BER than the MAP detector [40]. Further, the non‑
servations present in the dictionary at convergence. Fur‑
coherent detector based on concentration difference in 2
2
[49] has a computational complexity of O(N ). Further‑ thermore, a low complexity detection ≈ O(N ) was pro‑
s
s
more, the non‑linear detector in [69] offers less computa‑ posed in [72]. In [111], the non‑coherent detection based
tional complexity than the coherent MAP and MMSE de‑ on Fuzzy‑C means clustering gives a computational com‑
tectors. With the channel coding scheme used in [58], the plexity of O(SN k ) that is signi icantly less than the coher‑
complexity of maximum likelihood sequence detection is ent MAP detection. Here N k is the number of data points
O(Klog(log(S))) where K is the codeword length and in a cluster. Time complexity of the ANN based detec‑
d
∑
2
2
S is the number of available symbols at the transmitter. tor proposed in [27] was shown as O( i=1 n i−1 s f i m )
i
i
To reduce the complexity of decoding the convolutional where i is the index of a layer, d is the number of layers,
codes, Viterbi detector with asymmetric distance metric n i−1 is the number of input channels of the ith layer, s i is
has been proposed in [108]. The complexity of the re‑ the spatial size of ilter, f i is the number of ilters in the ith
ceiver in [75] is O(K/2). layer, and m i is the spatial size of the output feature. Fur‑
ther, in the Parzen‑PNN technique proposed by [30], the
Both decision feedback and the blind detectors had a lin‑ complexities related to computation, time and storage are
ear complexity in n in [65] but the blind detector is less O(dN s ), O(d), and O(dN s ), respectively. Here, d denotes
complex than the decision feedback detector since it does the dimension of the metrics and d = 3 was used in [30].
not needs the calculation of the complex decision met‑ The Parzen‑PNN‑based detector is less complex than the
ric and the statistical CSI. Here n denotes the sequence ANN‑based detectors. Table 3 summarizes the modula‑
length to be decoded. The CSI free detector proposed tion and detection techniques in static MC with drift in the
in [69] gives a complexity of O(SN s ). The MSSK mod‑ channel.
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 53