Page 62 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3 – Internet of Bio-Nano Things for health applications
P. 62
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3
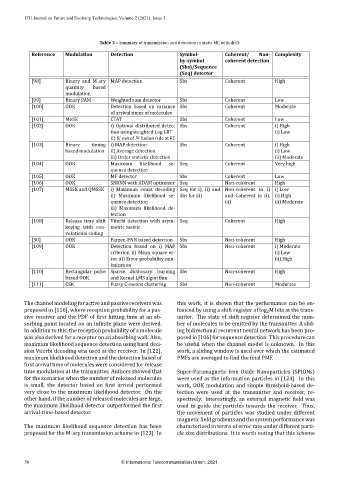
Table 3 – Summary of transmission and detection in static MC with drift
Reference Modulation Detection Symbol‑ Coherent/ Non‑ Complexity
by‑symbol coherent detection
(Sbs)/Sequence
(Seq) detector
[98] Binary and M‑ary MAP detection Sbs Coherent High
quantity based
modulation
[99] Binary PAM Weighted sum detector Sbs Coherent Low
[100] OOK Detection based on variance Sbs Coherent Moderate
of arrival times of molecules
[101] MoSK CTAT Sbs Coherent Low
[102] OOK i) Optimal distributed detec‑ Sbs Coherent i) High
tion using weighted Log LRT ii) Low
ii) K out of N fusion rule at FC
[103] Binary timing i) MAP detection Sbs Coherent i) High
based modulation ii) Average detection ii) Low
iii) Order statistic detection iii) Moderate
[104] OOK Maximum likelihood se‑ Seq Coherent Very high
quence detection
[105] OOK MF detector Sbs Coherent Low
[106] OOK SBRNN with ADAM optimizer Seq Non‑coherent High
[107] MSSK and QMSSK i) Maximum count decoding Seq for i), ii) and Non‑coherent in i) i) Low
ii) Maximum likelihood se‑ Sbs for iii) and Coherent in ii), ii) High
quence detection iii) iii) Moderate
iii) Maximum likelihood de‑
tection
[108] Release time shift Viterbi detection with asym‑ Seq Coherent High
keying with con‑ metric metric
volutional coding
[30] OOK Parzen‑PNN based detection Sbs Non‑coherent High
[109] OOK Detection based on i) MAP Sbs Non‑coherent i) Moderate
criterion ii) Mean square er‑ ii) Low
ror iii) Error probability min‑ iii) High
imization
[110] Rectangular pulse Sparse dictionary learning Sbs Non‑coherent High
based OOK and Kernel LMS algorithm
[111] CSK Fuzzy C‑means clustering Sbs Non‑coherent Moderate
The channel modeling for active and passive receivers was this work, it is shown that the performance can be en‑
proposed in [116], where reception probability for a pas‑ hanced by using a shift register of log 2 M bits at the trans‑
sive receiver and the PDF of irst hitting time at an ab‑ mitter. The state of shift register determined the num‑
sorbing point located on an in inite plane were derived. ber of molecules to be emitted by the transmitter. A slid‑
In addition to this, the reception probability of a molecule ing bidirectional recurrent neural network has been pro‑
was also derived for a receptor on an absorbing wall. Also, posedin[106]forsequencedetection. Thisprocedurecan
maximum likelihood sequence detection using hard deci‑ be useful when the channel model is unknown. In this
sion Viterbi decoding was used at the receiver. In [122], work, a sliding window is used over which the estimated
maximum likelihood detection and the detection based of PMFs are averaged to ind the inal PMF.
irst arrival time of molecules were considered for release
time modulation at the transmitter. Authors showed that Super‑Paramagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs)
for the scenarios when the number of released molecules were used as the information particles in [124]. In this
is small, the detector based on irst arrival performed work, OOK modulation and simple threshold‑based de‑
very close to the maximum likelihood detector. On the tection were used at the transmitter and receiver, re‑
other hand, if the number of released molecules are large, spectively. Interestingly, an external magnetic ield was
the maximum likelihood detector outperformed the irst used to guide the particles towards the receiver. Thus,
arrival‑time‑based detector. the movement of particles was studied under different
magnetic ield gradients and the system performance was
The maximum likelihood sequence detection has been characterized in terms of error rate under different parti‑
proposed for the M‑ary transmission scheme in [123]. In cle size distributions. It is worth noting that this scheme
50 © International Telecommunication Union, 2021