Page 61 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3 – Internet of Bio-Nano Things for health applications
P. 61
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3
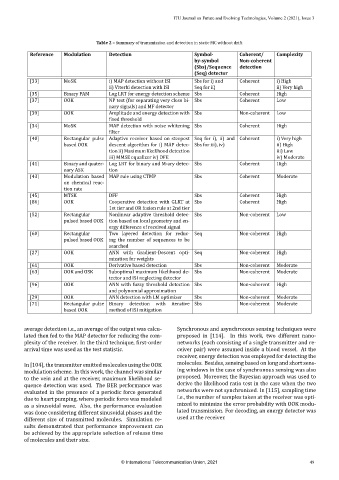
Table 2 – Summary of transmission and detection in static MC without drift
Reference Modulation Detection Symbol‑ Coherent/ Complexity
by‑symbol Non‑coherent
(Sbs)/Sequence detection
(Seq) detector
[33] MoSK i) MAP detection without ISI Sbs for i) and Coherent i) High
ii) Viterbi detection with ISI Seq for ii) ii) Very high
[35] Binary PAM Log LRT for energy detection scheme Sbs Coherent High
[37] OOK NP test (for separating very close bi‑ Sbs Coherent Low
nary signals) and MF detector
[39] OOK Amplitude and energy detection with Sbs Non‑coherent Low
ixed threshold
[34] MoSK MAP detection with noise whitening Sbs Coherent High
ilter
[40] Rectangular pulse Adaptive receiver based on steepest Seq for i), ii) and Coherent i) Very high
based OOK descent algorithm for i) MAP detec‑ Sbs for iii), iv) ii) High
tion ii) Maximum likelihood detection iii) Low
iii) MMSE equalizer iv) DFE iv) Moderate
[41] Binaryand quater‑ Log LRT for binary and M‑ary detec‑ Sbs Coherent High
nary ASK tion
[43] Modulation based MAP rule using CTMP Sbs Coherent Moderate
on chemical reac‑
tion rate
[45] MTSK DFF Sbs Coherent High
[86] OOK Cooperative detection with GLRT at Sbs Coherent High
1st tier and OR fusion rule at 2nd tier
[52] Rectangular Nonlinear adaptive threshold detec‑ Sbs Non‑coherent Low
pulsed based OOK tion based on local geometry and en‑
ergy difference of received signal
[60] Rectangular Two layered detection for reduc‑ Seq Non‑coherent High
pulsed based OOK ing the number of sequences to be
searched
[27] OOK ANN with Gradient‑Descent opti‑ Seq Non‑coherent High
mization for weights
[61] OOK Derivative based detection Sbs Non‑coherent Moderate
[63] OOK and OSK Suboptimal maximum likelihood de‑ Sbs Non‑coherent Moderate
tector and ISI neglecting detector
[96] OOK ANN with fuzzy threshold detection Sbs Non‑coherent High
and polynomial approximation
[29] OOK ANN detection with LM optimizer Sbs Non‑coherent Moderate
[71] Rectangular pulse Binary detection with iterative Sbs Non‑coherent Moderate
based OOK method of ISI mitigation
average detection i.e., an average of the output was calcu‑ Synchronous and asynchronous sensing techniques were
lated then fed to the MAP detector for reducing the com‑ proposed in [114]. In this work, two different nano‑
plexity of the receiver. In the third technique, irst‑order networks (each consisting of a single transmitter and re‑
arrival time was used as the test statistic. ceiver pair) were assumed inside a blood vessel. At the
receiver, energy detection was employed for detecting the
In [104], the transmitter emitted molecules using the OOK molecules. Besides, sensing based on long and short sens‑
modulation scheme. In this work, the channel was similar ing windows in the case of synchronous sensing was also
to the vein and at the receiver, maximum likelihood se‑ proposed. Moreover, the Bayesian approach was used to
derive the likelihood ratio test in the case when the two
quence detection was used. The BER performance was
networks were not synchronized. In [115], sampling time
evaluated in the presence of a periodic force generated
i.e., the number of samples taken at the receiver was opti‑
due to heart pumping, where periodic force was modeled
mized to minimize the error probability with OOK modu‑
as a sinusoidal wave. Also, the performance evaluation
lated transmission. For decoding, an energy detector was
was done considering different sinusoidal phases and the
used at the receiver.
different size of transmitted molecules. Simulation re‑
sults demonstrated that performance improvement can
be achieved by the appropriate selection of release time
of molecules and their size.
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 49