Page 63 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3 – Internet of Bio-Nano Things for health applications
P. 63
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3
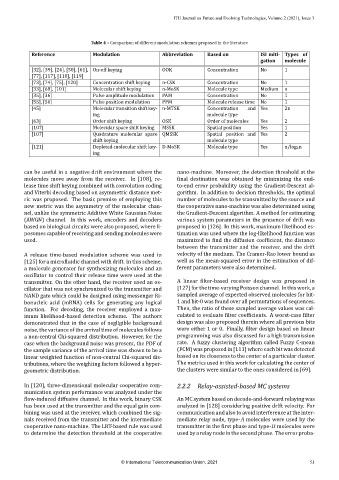
Table 4 – Comparison of different modulation schemes proposed in the literature
Reference Modulation Abbreviation Based on ISI miti‑ Types of
gation molecule
[32], [39], [24], [50], [61], On‑off keying OOK Concentration No 1
[77], [117], [118], [119]
[73], [74], [75], [120] Concentration shift keying n‑CSK Concentration No 1
[33], [68], [101] Molecular shift keying n‑MoSK Molecule type Medium n
[35], [36] Pulse amplitude modulation PAM Concentration No 1
[55], [56] Pulse position modulation PPM Molecule release time No 1
[45] Molecular transition shift key‑ n‑MTSK Concentration and Yes 2n
ing molecule type
[63] Order shift keying OSK Order of molecules Yes 2
[107] Molecular space shift keying MSSK Spatial position Yes 1
[107] Quadrature molecular space QMSSK Spatial position and Yes 2
shift keying molecule type
[121] Depleted‑molecular shift key‑ D‑MoSK Molecule type Yes n/log 2n
ing
can be useful in a negative drift environment where the nano‑machine. Moreover, the detection threshold at the
molecules move away from the receiver. In [108], re‑ inal destination was obtained by minimizing the end‑
lease time shift keying combined with convolution coding to‑end error probability using the Gradient‑Descent al‑
and Viterbi decoding based on asymmetric distance met‑ gorithm. In addition to decision thresholds, the optimal
ric was proposed. The basic premise of employing this number of molecules to be transmitted by the source and
new metric was the asymmetry of the molecular chan‑ the cooperative nano‑machine was also determined using
nel, unlike the symmetric Additive White Gaussian Noise the Gradient‑Descent algorithm. A method for estimating
(AWGN) channel. In this work, encoders and decoders various system parameters in the presence of drift was
based on biological circuits were also proposed, where li‑ proposed in [126]. In this work, maximum likelihood es‑
posomescapableofreceivingandsendingmoleculeswere timation was used where the log‑likelihood function was
used. maximized to ind the diffusion coef icient, the distance
between the transmitter and the receiver, and the drift
A release time‑based modulation scheme was used in velocity of the medium. The Cramer‑Rao lower bound as
[125] for a micro luidic channel with drift. In this scheme, well as the mean‑squared error in the estimation of dif‑
a molecule generator for synthesizing molecules and an ferent parameters were also determined.
oscillator to control their release time were used at the
transmitter. On the other hand, the receiver used an os‑ A linear ilter‑based receiver design was proposed in
cillator that was not synchronized to the transmitter and [127] for the time‑varying Poisson channel. In this work, a
NAND gate which could be designed using messenger Ri‑ sampled average of expected observed molecules for bit‑
bonucleic acid (mRNA) cells for generating any logical 1 and bit‑0 was found over all permutations of sequences.
function. For decoding, the receiver employed a max‑ Then, the ratio of these sampled average values was cal‑
imum likelihood‑based detection scheme. The authors culated to evaluate ilter coef icients. A worst‑case ilter
demonstrated that in the case of negligible background design was also proposed therein where all previous bits
noise, the variance of the arrival time of molecules follows were either 1 or 0. Finally, ilter design based on linear
a non‑central Chi‑squared distribution. However, for the programming was also discussed for a high transmission
case when the background noise was present, the PDF of rate. A fuzzy clustering algorithm called Fuzzy C‑mean
the sample variance of the arrival time was shown to be a (FCM) was proposed in [111] where each bit was detected
linear weighted function of non‑central Chi‑squared dis‑ based on its closeness to the center of a particular cluster.
tributions, where the weighting factors followed a hyper‑ The metrics used in this work for calculating the center of
geometric distribution. the clusters were similar to the ones considered in [69].
In [120], three‑dimensional molecular cooperative com‑ 2.2.2 Relay‑assisted‑based MC systems
munication system performance was analyzed under the
low‑induced diffusive channel. In this work, binary CSK An MC system based on decode‑and‑forward relaying was
has been used at the transmitter and the equal gain com‑ analyzed in [128] considering positive drift velocity. For
bining was used at the receiver, which combined the sig‑ communication and also to avoid interference at the inter‑
nals received from the transmitter and the intermediate mediate relay node, type‑A molecules were used by the
cooperative nano‑machine. The LRT‑based rule was used transmitter in the irst phase and type‑B molecules were
to determine the detection threshold at the cooperative used bya relaynode in the second phase. The errorproba‑
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 51