Page 15 - FIGI: Digital Financial Services security audit guideline
P. 15
(continued)
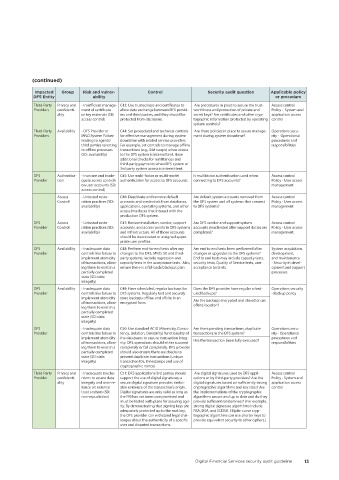
Impacted Group Risk and vulner- Control Security audit question Applicable policy
DFS Entity ability or procedure
Third-Party Privacy and - Insufficient manage- C43: Use trusted keys and certificates to Are procedures in place to assure the trust- Access control
Providers confidenti- ment of certificate allow data exchange between DFS provid- worthiness and protection of private and Policy - System and
ality or key materials (SD: ers and third parties, and they should be secret keys? Are certificates and other cryp- application access
access control) protected from disclosure. tographic information protected by operating control
system controls?
Third-Party Availability - DFS Provider or C44: Set procedural and technical controls Are there policies in place to assure manage- Operations secu-
Providers MNO System Failure for effective management during system ment during system downtime? rity - Operational
leading to agents/ downtime with related service providers. procedures and
third parties reverting For example, set controls to manage offline responsibilities
to offline processes transactions (e.g., SIM swaps) when access
(SD: availability) to the DFS system is intermittent. Have
additional checks for remittances and
third-party payments when DFS system or
3rd party system access is intermittent.
DFS Authentica- - Insecure and inade- C45: Use multi-factor or multi-model Is multifactor authentication used when Access control
Provider tion quate access controls authentication for access to DFS accounts. connecting to DFS accounts? Policy - User access
on user accounts (SD: management
access control)
Access - Untested resto- C46: Deactivate and remove default Are default system accounts removed from Access control
Control ration practices (SD: accounts and credentials from databases, the DFS system and all systems that connect Policy - User access
availability) applications, operating systems, and other to DFS systems? management
access interfaces that interact with the
production DFS system.
DFS Access - Untested resto- C47: Review installation, vendor, support Are DFS vendor and support system Access control
Provider Control ration practices (SD: accounts, and access points to DFS systems accounts deactivated after support duties are Policy - User access
availability) and infrastructure. All of those accounts completed? management
should be deactivated or assigned appro-
priate user profiles.
DFS Availability - Inadequate data C48: Perform end-to-end tests after any Are end to end tests been performed after System acquisition,
Provider controls like failure to changes to the DFS, MNO, SP, and third- changes or upgrades to the DFS systems? development,
implement atomicity party systems, include regression and End to end tests may include capacity tests, and maintenance
of transactions, allow- capacity tests in the acceptance tests. Also, security tests, Quality of Service tests, user - Security in devel-
ing them to exist in a ensure there is a fall-back/blackout plan. acceptance tests etc. opment and support
partially completed processes
state (SD: data
integrity)
DFS Availability - Inadequate data C49: Have scheduled, regular backups for Does the DFS provider have regular sched- Operations security
Provider controls like failure to DFS systems. Regularly test and securely uled backups? - Backup policy
implement atomicity store backups offline and offsite in an Are the backups encrypted and stored on an
of transactions, allow- encrypted form. offsite location?
ing them to exist in a
partially completed
state (SD: data
integrity)
DFS - Inadequate data C50: Use standard ACID (Atomicity, Consis- Are there pending transactions, duplicate Operations secu-
Provider controls like failure to tency, Isolation, Durability) functionality of transactions in the DFS system? rity - Operational
implement atomicity the databases to ensure transaction integ- Has the transaction been fully executed? procedures and
of transactions, allow- rity. DFS operations should either succeed responsibilities
ing them to exist in a completely or fail completely. DFS provider
partially completed should also ensure there are checks to
state (SD: data prevent duplicate transactions (unique
integrity) transaction IDs, timestamps and use of
cryptographic nonce)
Third-Party Privacy and - Inadequate mecha- C51: DFS applications/3rd parties should Are digital signatures used by DFS appli- Access control
Provider confidenti- nisms to assure data support the use of digital signatures; a cations or by third-party providers? Are the Policy - System and
ality integrity and over-re- secure digital signature provides irrefut- digital signatures based on sufficiently strong application access
liance on external able evidence of the transaction's origin. cryptographic algorithms and key sizes? Are control
trust anchors (SD: Digital signatures are only valid as long as the implementations of the cryptographic
non-repudiation) the PKI has not been compromised and algorithms secure and up to date and do they
must be tested with plans for assuring agil- provide sufficient randomness? (For example,
ity. By demonstrating that signing keys are strong digital signature algorithms include
adequately protected up to the root key, RSA, DSA, and ECDSA. Elliptic-curve cryp-
the DFS provider can withstand legal chal- tographic algorithms can use shorter keys to
lenges about the authenticity of a specific provide equivalent security to other ciphers.)
user and disputed transactions.
Digital Financial Services security audit guideline 13