Page 13 - FIGI: Digital Financial Services security audit guideline
P. 13
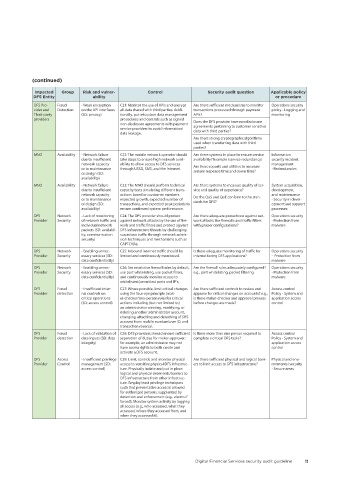
(continued)
Impacted Group Risk and vulner- Control Security audit question Applicable policy
DFS Entity ability or procedure
DFS Pro- Fraud - Weak encryption C21: Monitor the use of APIs and encrypt Are there sufficient mechanisms to monitor Operations security
vider and Detection on the API interfaces all data shared with third parties. Addi- transactions processed through payment policy - Logging and
Third-party (SD: privacy) tionally, put into place data management APIs? monitoring
providers procedures and controls such as signed
non-disclosure agreements with payment Does the DFS provider have nondisclosure
service providers to avoid information/ agreements pertaining to customer sensitive
data with third parties?
data leakage.
Are there strong cryptographic algorithms
used when transferring data with third
parties?
MNO Availability - Network failure C22: The mobile network operator should Are there systems in place to ensure service Information
due to insufficient take steps to ensure high network avail- availability? Example (service redundancy) security incident
network capacity ability to allow access to DFS services Are there reports and utilities to measure management
or to maintenance through USSD, SMS, and the Internet. system response time and down time? - Redundancies
or design (SD:
availability)
MNO Availability - Network failure C23: The MNO should perform technical Are there systems to measure quality of ser- System acquisition,
due to insufficient capacity tests simulating different trans- vice and quality of experience? development,
network capacity actions based on customer numbers, and maintenance
or to maintenance expected growth, expected number of Do the QoS and QoE conform to the stan- - Security in devel-
dards for DFS?
or design (SD: transactions, and expected peak periods to opment and support
availability) ensure continued system performance. processes
DFS Network - Lack of monitoring C24: The DFS provider should protect Are there adequate protections against net- Operations security
Provider Security of network traffic and against network attacks by the use of fire- work attacks like firewalls and traffic filters - Protection from
individual network walls and traffic filters and protect against with proper configurations? malware
packets (SD: availabil- DFS infrastructure threats by challenging
ity, communication suspicious traffic through network admis-
security) sion techniques and mechanisms such as
CAPTCHAs.
DFS Network - Enabling unnec- C25: Inbound internet traffic should be Is there adequate monitoring of traffic for Operations security
Provider Security essary services (SD: limited and continuously monitored. internet facing DFS applications? - Protection from
data confidentiality) malware
DFS Network - Enabling unnec- C26: Set restrictive firewall rules by default, Are the firewall rules adequately configured? Operations security
Provider Security essary services (SD: use port whitelisting, use packet filters, e.g., port whitelisting, packet filtering - Protection from
data confidentiality) and continuously monitor access to malware
whitelisted/permitted ports and IP's.
DFS Fraud - Insufficient inter- C27: Where possible, limit critical changes Are there sufficient controls to review and Access control
Provider detection nal controls on using the four-eye principle (mak- approve for critical changes on accounts? e.g., Policy - System and
critical operations er-checker/two-person rule) for critical is there maker-checker and approval process application access
(SD: access control) actions including (but not limited to) before changes are made? control
an administrator creating, modifying, or
deleting another administrator account,
changing, attaching and detaching of DFS
account from mobile number/user ID, and
transaction reversal.
DFS Fraud - Lack of validation of C28: DFS providers should ensure sufficient Is there more than one person required to Access control
Provider detection data inputs (SD: data separation of duties for maker-approver; complete a critical DFS tasks? Policy - System and
integrity) for example, an administrator may not application access
have access rights to both create and control
activate a DFS account.
DFS Access - Insufficient privilege C29: Limit, control, and monitor physical Are there sufficient physical and logical barri- Physical and envi-
Provider Control management (SD: access to sensitive physical DFS infrastruc- ers to limit access to DFS infrastructure? ronmental security
access control) ture. Physically isolate and put in place - Secure areas
logical and physical deterrents/barriers to
DFS infrastructure from other infrastruc-
ture. Employ least privilege techniques
such that preventative access is allowed
for authorized persons, supplanted by
detection and enforcement (e.g., alarms if
forced). Monitor system activity by logging
all access (e.g., who accessed, what they
accessed, where they accessed from, and
when they accessed it).
Digital Financial Services security audit guideline 11