Page 61 - FIGI: Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies
P. 61
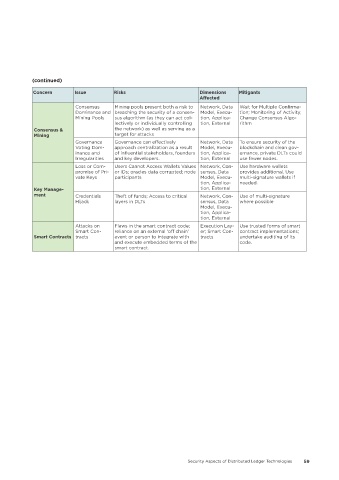
(continued)
Concern Issue Risks Dimensions Mitigants
Affected
Consensus Mining pools present both a risk to Network, Data Wait for Multiple Confirma-
Dominance and breaching the security of a consen- Model, Execu- tion; Monitoring of Activity;
Mining Pools sus algorithm (as they can act col- tion, Applica- Change Consensus Algo-
lectively or individually controlling tion, External rithm
Consensus & the network) as well as serving as a
Mining target for attacks
Governance Governance can effectively Network, Data To ensure security of the
Voting Dom- approach centralization as a result Model, Execu- blockchain and clean gov-
inance and of influential stakeholders, founders tion, Applica- ernance, private DLTs could
Irregularities and key developers. tion, External use fewer nodes.
Loss or Com- Users Cannot Access Wallets Values Network, Con- Use hardware wallets
promise of Pri- or IDs; oracles data corrupted; node sensus, Data provides additional. Use
vate Keys participants Model, Execu- multi-signature wallets if
tion, Applica- needed.
Key Manage- tion, External
ment Credentials Theft of funds; Access to critical Network, Con- Use of multi-signature
Hijack layers in DLTs sensus, Data where possible
Model, Execu-
tion, Applica-
tion, External
Attacks on Flaws in the smart contract code; Execution Lay- Use trusted forms of smart
Smart Con- reliance on an external ‘off chain’ er; Smart Con- contract implementations;
Smart Contracts tracts event or person to integrate with tracts undertake auditing of its
and execute embedded terms of the code.
smart contract.
Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies 59