Page 59 - FIGI: Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies
P. 59
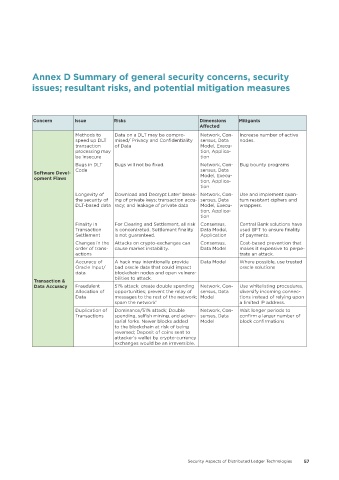
Annex D Summary of general security concerns, security
issues; resultant risks, and potential mitigation measures
Concern Issue Risks Dimensions Mitigants
Affected
Methods to Data on a DLT may be compro- Network, Con- Increase number of active
speed up DLT mised/ Privacy and Confidentiality sensus, Data nodes.
transaction of Data Model, Execu-
processing may tion, Applica-
be insecure tion
Bugs in DLT Bugs will not be fixed. Network, Con- Bug bounty programs
Code sensus, Data
Software Devel-
opment Flaws Model, Execu-
tion, Applica-
tion
Longevity of Download and Decrypt Later’ break- Network, Con- Use and implement quan-
the security of ing of private keys; transaction accu- sensus, Data tum resistant ciphers and
DLT-based data racy; and leakage of private data Model, Execu- wrappers.
tion, Applica-
tion
Finality in For Clearing and Settlement, all risk Consensus, Central Bank solutions have
Transaction is concentrated. Settlement finality Data Model, used BFT to ensure finality
Settlement is not guaranteed. Application of payments.
Changes in the Attacks on crypto-exchanges can Consensus, Cost-based prevention that
order of trans- cause market instability. Data Model makes it expensive to perpe-
actions trate an attack.
Accuracy of A hack may intentionally provide Data Model Where possible, use trusted
Oracle Input/ bad oracle data that could impact oracle solutions
data blockchain nodes and open vulnera-
Transaction & bilities to attack.
Data Accuracy Fraudulent 51% attack; create double spending Network, Con- Use whitelisting procedures,
Allocation of opportunities; prevent the relay of sensus, Data diversify incoming connec-
Data messages to the rest of the network; Model tions instead of relying upon
spam the network’ a limited IP address.
Duplication of Dominance/51% attack; Double Network, Con- Wait longer periods to
Transactions spending, selfish mining, and adver- sensus, Data confirm a larger number of
sarial forks. Newer blocks added Model block confirmations
to the blockchain at risk of being
reversed; Deposit of coins sent to
attacker’s wallet by crypto-currency
exchanges would be an irreversible.
Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies 57