Page 29 - FIGI: Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies
P. 29
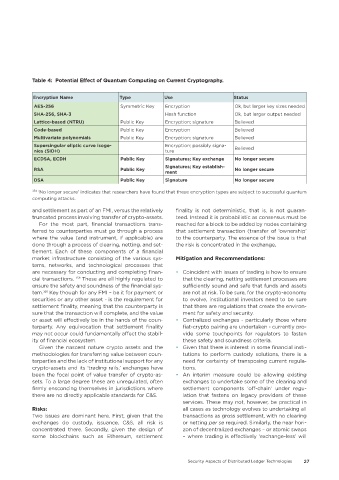
Table 4: Potential Effect of Quantum Computing on Current Cryptography�
Encryption Name Type Use Status
AES-256 Symmetric Key Encryption Ok, but larger key sizes needed
SHA-256, SHA-3 Hash function Ok, but larger output needed
Lattice-based (NTRU) Public Key Encryption; signature Believed
Code-based Public Key Encryption Believed
Multivariate polynomials Public Key Encryption; signature Believed
Supersingular ellptic curve isoge- Encryption; possibly signa-
nies (SIDH) ture Believed
ECDSA, ECDH Public Key Signatures; Key exchange No longer secure
Signatures; Key establish-
RSA Public Key No longer secure
ment
DSA Public Key Signature No longer secure
154 ‘No longer secure’ indicates that researchers have found that these encryption types are subject to successful quantum
computing attacks.
and settlement as part of an FMI, versus the relatively finality is not deterministic, that is, is not guaran-
truncated process involving transfer of crypto-assets. teed. Instead it is probabilistic as consensus must be
For the most part, financial transactions trans- reached for a block to be added by nodes containing
ferred to counterparties must go through a process that settlement transaction (transfer of ‘ownership’
where the value (and instrument, if applicable) are to the counterparty. The essence of the issue is that
done through a process of clearing, netting, and set- the risk is concentrated in the exchange,
tlement. Each of these components of a financial
market infrastructure consisting of the various sys- Mitigation and Recommendations:
tems, networks, and technological processes that
are necessary for conducting and completing finan- • Coincident with issues of trading is how to ensure
cial transactions. These are all highly regulated to that the clearing, netting settlement processes are
159
ensure the safety and soundness of the financial sys- sufficiently sound and safe that funds and assets
tem. Key though for any FMI – be it for payment or are not at risk. To be sure, for the crypto-economy
160
securities or any other asset - is the requirement for to evolve, institutional investors need to be sure
settlement finality, meaning that the counterparty is that there are regulations that create the environ-
sure that the transaction will complete, and the value ment for safety and security.
or asset will effectively be in the hands of the coun- • Centralized exchanges - particularly those where
terparty. Any equivocation that settlement finality fiat-crypto pairing are undertaken - currently pro-
may not occur could fundamentally affect the stabil- vide some touchpoints for regulators to fasten
ity of financial ecosystem. these safety and soundness criteria.
Given the nascent nature crypto assets and the • Given that there is interest in some financial insti-
methodologies for transferring value between coun- tutions to perform custody solutions, there is a
terparties and the lack of institutional support for any need for certainty of transposing current regula-
crypto-assets and its ‘trading rails,’ exchanges have tions.
been the focal point of value transfer of crypto-as- • An interim measure could be allowing existing
sets. To a large degree these are unregulated, often exchanges to undertake some of the clearing and
firmly ensconcing themselves in jurisdictions where settlement components ‘off-chain’ under regu-
there are no directly applicable standards for C&S. lation that fastens on legacy providers of these
services. These may not, however, be practical in
Risks: all cases as technology evolves to undertaking all
Two issues are dominant here. First, given that the transactions as gross settlement, with no clearing
exchanges do custody, issuance, C&S, all risk is or netting per se required. Similarly, the near hori-
concentrated there. Secondly, given the design of zon of decentralized exchanges – or atomic swaps
some blockchains such as Ethereum, settlement – where trading is effectively ‘exchange-less’ will
Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies 27