Page 33 - FIGI: Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies
P. 33
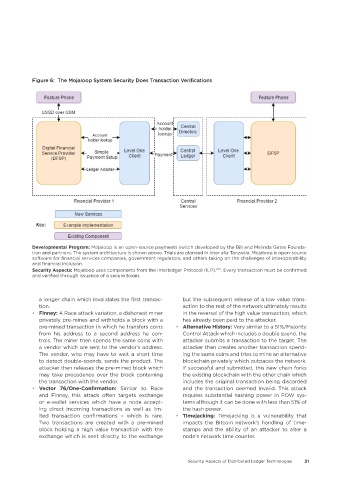
Figure 6: The Mojaloop System Security Does Transaction Verifications
Developmental Program: Mojaloop is an open-source payments switch developed by the Bill and Melinda Gates Founda-
tion and partners. The system architecture is shown above. Trials are planned in inter alia Tanzania. Mojaloop is open-source
software for financial services companies, government regulators, and others taking on the challenges of interoperability
and financial inclusion.
Security Aspects: Mojaloop uses components from the Interledger Protocol (ILP). 207 . Every transaction must be confirmed
and verified through issuance of a secure token.
a longer chain which invalidates the first transac- but the subsequent release of a low value trans-
tion. action to the rest of the network ultimately results
• Finney: A Race attack variation, a dishonest miner in the reversal of the high value transaction, which
privately pre-mines and withholds a block with a has already been paid to the attacker.
pre-mined transaction in which he transfers coins • Alternative History: Very similar to a 51%/Majority
from his address to a second address he con- Control Attack which includes a double spend, the
trols. The miner then spends the same coins with attacker submits a transaction to the target. The
a vendor which are sent to the vendor’s address. attacker then creates another transaction spend-
The vendor, who may have to wait a short time ing the same coins and tries to mine an alternative
to detect double-spends, sends the product. The blockchain privately which outpaces the network.
attacker then releases the pre-mined block which If successful and submitted, this new chain forks
may take precedence over the block containing the existing blockchain with the other chain which
the transaction with the vendor. includes the original transaction being discarded
• Vector 76/One-Confirmation: Similar to Race and the transaction deemed invalid. This attack
and Finney, this attack often targets exchange requires substantial hashing power in POW sys-
or e-wallet services which have a node accept- tems although it can be done with less than 51% of
ing direct incoming transactions as well as lim- the hash power.
ited transaction confirmations – which is rare. • Timejacking: Timejacking is a vulnerability that
Two transactions are created with a pre-mined impacts the Bitcoin network’s handling of time-
block holding a high value transaction with the stamps and the ability of an attacker to alter a
exchange which is sent directly to the exchange node's network time counter.
Security Aspects of Distributed Ledger Technologies 31