Page 38 - Implementation of Secure Authentication Technologies for Digital Financial Services
P. 38
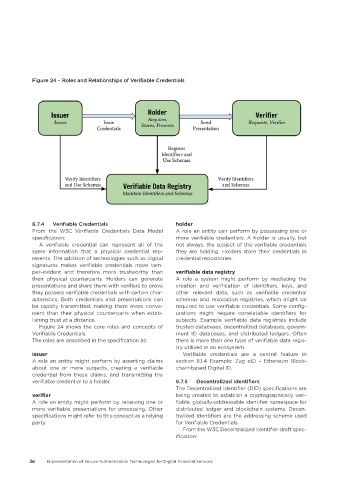
Figure 24 – Roles and Relationships of Verifiable Credentials
6.7.4 Verifiable Credentials holder
From the W3C Verifiable Credentials Data Model A role an entity can perform by possessing one or
specification: more verifiable credentials. A holder is usually, but
A verifiable credential can represent all of the not always, the subject of the verifiable credentials
same information that a physical credential rep- they are holding. Holders store their credentials in
resents. The addition of technologies such as digital credential repositories.
signatures makes verifiable credentials more tam-
per-evident and therefore more trustworthy than verifiable data registry
their physical counterparts. Holders can generate A role a system might perform by mediating the
presentations and share them with verifiers to prove creation and verification of identifiers, keys, and
they possess verifiable credentials with certain char- other relevant data, such as verifiable credential
acteristics. Both credentials and presentations can schemas and revocation registries, which might be
be rapidly transmitted, making them more conve- required to use verifiable credentials. Some config-
nient than their physical counterparts when estab- urations might require correlatable identifiers for
lishing trust at a distance. subjects. Example verifiable data registries include
Figure 24 shows the core roles and concepts of trusted databases, decentralized databases, govern-
Verifiable Credentials. ment ID databases, and distributed ledgers. Often
The roles are described in the specification as: there is more than one type of verifiable data regis-
try utilized in an ecosystem.
issuer Verifiable credentials are a central feature in
A role an entity might perform by asserting claims section 8.1.4 Example: Zug eID – Ethereum Block-
about one or more subjects, creating a verifiable chain-based Digital ID.
credential from these claims, and transmitting the
verifiable credential to a holder. 6.7.5 Decentralized Identifiers
The Decentralized Identifier (DID) specifications are
verifier being created to establish a cryptographically veri-
A role an entity might perform by receiving one or fiable, globally-addressable identifier namespace for
more verifiable presentations for processing. Other distributed ledger and blockchain systems. Decen-
specifications might refer to this concept as a relying tralized Identifiers are the addressing scheme used
party. for Verifiable Credentials.
From the W3C Decentralized Identifier draft spec-
ification:
36 Implementation of Secure Authentication Technologies for Digital Financial Services