Page 40 - Use cases and requirements for the vehicular multimedia networks - Focus Group on Vehicular Multimedia (FG-VM)
P. 40
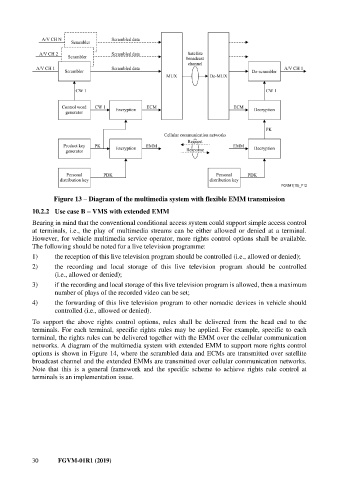
Figure 13 – Diagram of the multimedia system with flexible EMM transmission
10.2.2 Use case B – VMS with extended EMM
Bearing in mind that the conventional conditional access system could support simple access control
at terminals, i.e., the play of multimedia streams can be either allowed or denied at a terminal.
However, for vehicle multimedia service operator, more rights control options shall be available.
The following should be noted for a live television programme:
1) the reception of this live television program should be controlled (i.e., allowed or denied);
2) the recording and local storage of this live television program should be controlled
(i.e., allowed or denied);
3) if the recording and local storage of this live television program is allowed, then a maximum
number of plays of the recorded video can be set;
4) the forwarding of this live television program to other nomadic devices in vehicle should
controlled (i.e., allowed or denied).
To support the above rights control options, rules shall be delivered from the head end to the
terminals. For each terminal, specific rights rules may be applied. For example, specific to each
terminal, the rights rules can be delivered together with the EMM over the cellular communication
networks. A diagram of the multimedia system with extended EMM to support more rights control
options is shown in Figure 14, where the scrambled data and ECMs are transmitted over satellite
broadcast channel and the extended EMMs are transmitted over cellular communication networks.
Note that this is a general framework and the specific scheme to achieve rights rule control at
terminals is an implementation issue.
30 FGVM-01R1 (2019)