Page 966 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 966
6 Monitoring
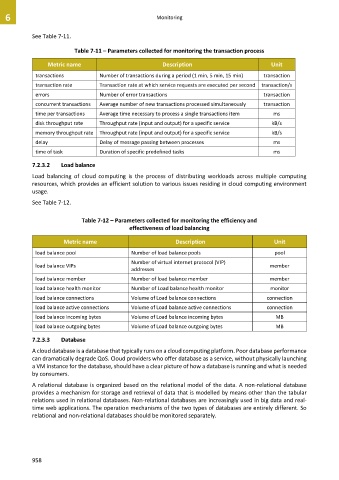
See Table 7-11.
Table 7-11 – Parameters collected for monitoring the transaction process
Metric name Description Unit
transactions Number of transactions during a period (1 min, 5 min, 15 min) transaction
transaction rate Transaction rate at which service requests are executed per second transaction/s
errors Number of error transactions transaction
concurrent transactions Average number of new transactions processed simultaneously transaction
time per transactions Average time necessary to process a single transactions item ms
disk throughput rate Throughput rate (input and output) for a specific service kB/s
memory throughput rate Throughput rate (input and output) for a specific service kB/s
delay Delay of message passing between processes ms
time of task Duration of specific predefined tasks ms
7.2.3.2 Load balance
Load balancing of cloud computing is the process of distributing workloads across multiple computing
resources, which provides an efficient solution to various issues residing in cloud computing environment
usage.
See Table 7-12.
Table 7-12 – Parameters collected for monitoring the efficiency and
effectiveness of load balancing
Metric name Description Unit
load balance pool Number of load balance pools pool
Number of virtual internet protocol (VIP)
load balance VIPs member
addresses
load balance member Number of load balance member member
load balance health monitor Number of Load balance health monitor monitor
load balance connections Volume of Load balance connections connection
load balance active connections Volume of Load balance active connections connection
load balance incoming bytes Volume of Load balance incoming bytes MB
load balance outgoing bytes Volume of Load balance outgoing bytes MB
7.2.3.3 Database
A cloud database is a database that typically runs on a cloud computing platform. Poor database performance
can dramatically degrade QoS. Cloud providers who offer database as a service, without physically launching
a VM instance for the database, should have a clear picture of how a database is running and what is needed
by consumers.
A relational database is organized based on the relational model of the data. A non-relational database
provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modelled by means other than the tabular
relations used in relational databases. Non-relational databases are increasingly used in big data and real-
time web applications. The operation mechanisms of the two types of databases are entirely different. So
relational and non-relational databases should be monitored separately.
958