Page 965 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 965
Monitoring 6
7.2.2 Service availability
Service availability is the property of being accessible and usable upon demand by an authorized entity.
Continuity is the key feature used to measure service availability, which ensures the service is available for a
certain amount of time without any interruption. Furthermore, if there is an incident, continuity enables the
service to be restarted and access to data and functionality of the service regained within a particular period.
All elements, including computing, storage, network and power supplement, can affect service continuity.
For example, for a public-cloud end user, availability of the cloud not only refers to the services provided by
the cloud service provider, but also to the possibility of accessing those services remotely.
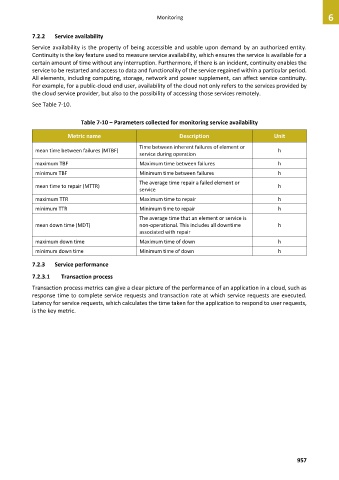
See Table 7-10.
Table 7-10 – Parameters collected for monitoring service availability
Metric name Description Unit
Time between inherent failures of element or
mean time between failures (MTBF) h
service during operation
maximum TBF Maximum time between failures h
minimum TBF Minimum time between failures h
The average time repair a failed element or
mean time to repair (MTTR) h
service
maximum TTR Maximum time to repair h
minimum TTR Minimum time to repair h
The average time that an element or service is
mean down time (MDT) non-operational. This includes all downtime h
associated with repair
maximum down time Maximum time of down h
minimum down time Minimum time of down h
7.2.3 Service performance
7.2.3.1 Transaction process
Transaction process metrics can give a clear picture of the performance of an application in a cloud, such as
response time to complete service requests and transaction rate at which service requests are executed.
Latency for service requests, which calculates the time taken for the application to respond to user requests,
is the key metric.
957