Page 963 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 963
Monitoring 6
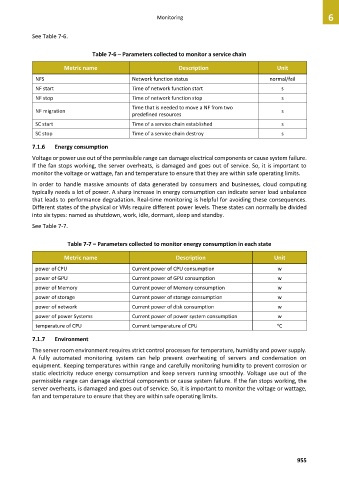
See Table 7-6.
Table 7-6 – Parameters collected to monitor a service chain
Metric name Description Unit
NFS Network function status normal/fail
NF start Time of network function start s
NF stop Time of network function stop s
Time that is needed to move a NF from two
NF migration s
predefined resources
SC start Time of a service chain established s
SC stop Time of a service chain destroy s
7.1.6 Energy consumption
Voltage or power use out of the permissible range can damage electrical components or cause system failure.
If the fan stops working, the server overheats, is damaged and goes out of service. So, it is important to
monitor the voltage or wattage, fan and temperature to ensure that they are within safe operating limits.
In order to handle massive amounts of data generated by consumers and businesses, cloud computing
typically needs a lot of power. A sharp increase in energy consumption can indicate server load unbalance
that leads to performance degradation. Real-time monitoring is helpful for avoiding these consequences.
Different states of the physical or VMs require different power levels. These states can normally be divided
into six types: named as shutdown, work, idle, dormant, sleep and standby.
See Table 7-7.
Table 7-7 – Parameters collected to monitor energy consumption in each state
Metric name Description Unit
power of CPU Current power of CPU consumption w
power of GPU Current power of GPU consumption w
power of Memory Current power of Memory consumption w
power of storage Current power of storage consumption w
power of network Current power of disk consumption w
power of power Systems Current power of power system consumption w
temperature of CPU Current temperature of CPU o C
7.1.7 Environment
The server room environment requires strict control processes for temperature, humidity and power supply.
A fully automated monitoring system can help prevent overheating of servers and condensation on
equipment. Keeping temperatures within range and carefully monitoring humidity to prevent corrosion or
static electricity reduce energy consumption and keep servers running smoothly. Voltage use out of the
permissible range can damage electrical components or cause system failure. If the fan stops working, the
server overheats, is damaged and goes out of service. So, it is important to monitor the voltage or wattage,
fan and temperature to ensure that they are within safe operating limits.
955