Page 961 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 961
Monitoring 6
7.1.4 Network
High-performance computing requires large amounts of network bandwidth. Particularly for cloud
computing, the network has a strong meaning, as all provided resources and services are available through a
network. It has been found that poor network performance is caused by virtualization I/O overhead. A
network monitoring system helps in realization of traffic, utilization and errors and then, based on accurate
monitoring information, quality of service (QoS) policy validation, network outage resolution, performance
problem troubleshooting, and in making important capacity planning decisions.
See Table 7-4.
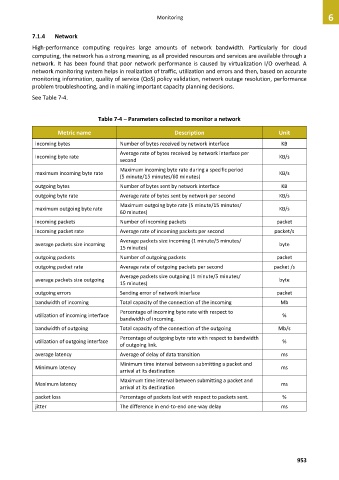
Table 7-4 – Parameters collected to monitor a network
Metric name Description Unit
incoming bytes Number of bytes received by network interface KB
Average rate of bytes received by network interface per
incoming byte rate KB/s
second
Maximum incoming byte rate during a specific period
maximum incoming byte rate KB/s
(5 minute/15 minutes/60 minutes)
outgoing bytes Number of bytes sent by network interface KB
outgoing byte rate Average rate of bytes sent by network per second KB/s
Maximum outgoing byte rate (5 minute/15 minutes/
maximum outgoing byte rate KB/s
60 minutes)
incoming packets Number of incoming packets packet
incoming packet rate Average rate of incoming packets per second packet/s
Average packets size incoming (1 minute/5 minutes/
average packets size incoming byte
15 minutes)
outgoing packets Number of outgoing packets packet
outgoing packet rate Average rate of outgoing packets per second packet /s
Average packets size outgoing (1 minute/5 minutes/
average packets size outgoing byte
15 minutes)
outgoing errors Sending error of network interface packet
bandwidth of incoming Total capacity of the connection of the incoming Mb
Percentage of incoming byte rate with respect to
utilization of incoming interface %
bandwidth of incoming.
bandwidth of outgoing Total capacity of the connection of the outgoing Mb/s
Percentage of outgoing byte rate with respect to bandwidth
utilization of outgoing interface %
of outgoing link.
average latency Average of delay of data transition ms
Minimum time interval between submitting a packet and
Minimum latency ms
arrival at its destination
Maximum time interval between submitting a packet and
Maximum latency ms
arrival at its destination
packet loss Percentage of packets lost with respect to packets sent. %
jitter The difference in end-to-end one-way delay ms
953