Page 246 - Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications
P. 246
5 Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications
6.11 Big-data-driven cross-layer design
Traditionally, networking is divided into different layers, and a set of protocols is used to communicate
between adjacent layers. In traditional layered design, direct communications between non-adjacent layers
are forbidden. However, recent advances in cross-layer designs show that non-adjacent layers can share
information during run-time, which will result in new algorithms and significantly improved performance in
networking systems. Although sharing information among different layers can improve performance, the
principle of modularity is broken and the network becomes so complex that traditional approaches are
inadequate to design and optimize it.
Fortunately, bDDN can benefit cross-layer design. The logically centralized controller in bDDN has a global
view of the network, which enables it to obtain big data from all layers with arbitrary granularity, such as
channel state information in the physical layer, packet information in the data link/network layers and
application information in the application layer. Applying big data technologies to network control and
management can significantly improve network control and management processes.
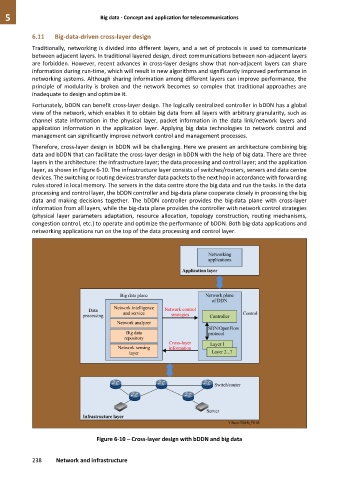
Therefore, cross-layer design in bDDN will be challenging. Here we present an architecture combining big
data and bDDN that can facilitate the cross-layer design in bDDN with the help of big data. There are three
layers in the architecture: the infrastructure layer; the data processing and control layer; and the application
layer, as shown in Figure 6-10. The infrastructure layer consists of switches/routers, servers and data centre
devices. The switching or routing devices transfer data packets to the next hop in accordance with forwarding
rules stored in local memory. The servers in the data centre store the big data and run the tasks. In the data
processing and control layer, the bDDN controller and big-data plane cooperate closely in processing the big
data and making decisions together. The bDDN controller provides the big-data plane with cross-layer
information from all layers, while the big-data plane provides the controller with network control strategies
(physical layer parameters adaptation, resource allocation, topology construction, routing mechanisms,
congestion control, etc.) to operate and optimize the performance of bDDN. Both big-data applications and
networking applications run on the top of the data processing and control layer.
Figure 6-10 – Cross-layer design with bDDN and big data
238 Network and infrastructure