Page 245 - Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications
P. 245
Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications 5
6.9.1.3 Data intelligence and mobile network planning
All base stations can be compared based on comprehensive experience, and the poor ones identified. Some
statistical modules can calculate which base stations are poor. The decision to expand the capacity of poor
base stations or to build new ones nearby can be made accurately based on service demand estimates.
6.10 Big-data-driven traffic engineering
Traffic engineering is an important method of optimizing network performance by dynamically analysing,
predicting and regulating the behaviour of data transmitted over that network. Typical objectives of traffic
engineering include balancing network load and maximizing network utilization. bDDN and big data-analytics
provide a convenient and effective way to perform traffic engineering and improve network performance on
a large scale. Typically, a software-defined networking (SDN) based network consists of thousands of hosts
with significant bandwidth requirements. Traffic engineering in such networks is very challenging. The big-
data plane in bDDN for traffic engineering is an apt solution for the following reasons:
1) it is relatively easy to obtain big data traffic and failure information via a logically centralized network
controller;
2) any flow format of big traffic data with arbitrary granularity can be exploited for traffic engineering;
3) it is relatively easier to apply traffic engineering results to switches in a data centre network by
modifying flow tables within the switches.
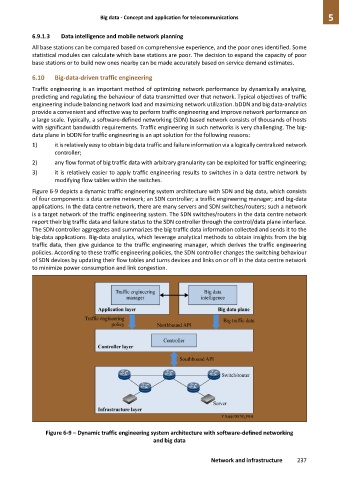
Figure 6-9 depicts a dynamic traffic engineering system architecture with SDN and big data, which consists
of four components: a data centre network; an SDN controller; a traffic engineering manager; and big-data
applications. In the data centre network, there are many servers and SDN switches/routers; such a network
is a target network of the traffic engineering system. The SDN switches/routers in the data centre network
report their big traffic data and failure status to the SDN controller through the control/data plane interface.
The SDN controller aggregates and summarizes the big traffic data information collected and sends it to the
big-data applications. Big-data analytics, which leverage analytical methods to obtain insights from the big
traffic data, then give guidance to the traffic engineering manager, which derives the traffic engineering
policies. According to these traffic engineering policies, the SDN controller changes the switching behaviour
of SDN devices by updating their flow tables and turns devices and links on or off in the data centre network
to minimize power consumption and link congestion.
Figure 6-9 – Dynamic traffic engineering system architecture with software-defined networking
and big data
Network and infrastructure 237