Page 145 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 145
ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables 3
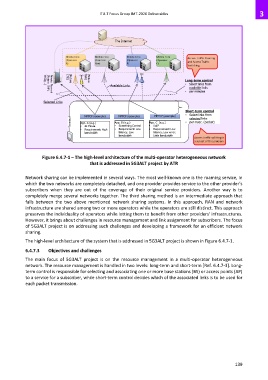
Figure 6.4.7-1 – The high-level architecture of the multi-operator heterogeneous network
that is addressed in 5G3ALT project by ATR
Network sharing can be implemented in several ways. The most well-known one is the roaming service, in
which the two networks are completely detached, and one provider provides service to the other provider’s
subscribers when they are out of the coverage of their original service providers. Another way is to
completely merge several networks together. The third sharing method is an intermediate approach that
falls between the two above mentioned network sharing systems. In this approach, RAN and network
infrastructure are shared among two or more operators while the operators are still distinct. This approach
preserves the individuality of operators while letting them to benefit from other providers’ infrastructures.
However, it brings about challenges in resource management and link assignment for subscribers. The focus
of 5G3ALT project is on addressing such challenges and developing a framework for an efficient network
sharing.
The high-level architecture of the system that is addressed in 5G3ALT project is shown in Figure 6.4.7-1.
6.4.7.3 Objectives and challenges
The main focus of 5G3ALT project is on the resource management in a multi-operator heterogeneous
network. The resource management is handled in two levels: long-term and short-term [Ref. 6.4.7-3]. Long-
term control is responsible for selecting and associating one or more base stations (BS) or access points (AP)
to a service for a subscriber, while short-term control decides which of the associated links is to be used for
each packet transmission.
139