Page 140 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 140
3 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
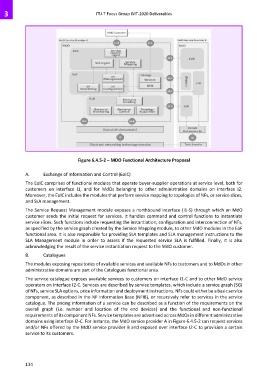
Figure 6.4.5-2 – MDO Functional Architecture Proposal
A. Exchange of Information and Control (EoIC)
The EoIC comprises of functional modules that operate buyer-supplier operations at service level, both for
customers on interface I1, and for MdOs belonging to other administrative domains on interface I2.
Moreover, the EoIC includes the modules that perform service mapping to topologies of NFs, or service slices,
and SLA management.
The Service Request Management module exposes a northbound interface (I1-S) through which an MdO
customer sends the initial request for services. It handles command and control functions to instantiate
service slices. Such functions include requesting the instantiation, configuration and interconnection of NFs,
as specified by the service graph created by the Service Mapping module, to other MdO modules in the EoF
functional area. It is also responsible for providing SLA templates and SLA management instructions to the
SLA Management module in order to assess if the requested service SLA is fulfilled. Finally, it is also
acknowledging the result of the service instantiation request to the MdO customer.
B. Catalogues
The modules exposing repositories of available services and available NFs to customers and to MdOs in other
administrative domains are part of the Catalogues functional area.
The service catalogue exposes available services to customers on interface I1-C and to other MdO service
operators on interface I2-C. Services are described by service templates, which include a service graph (SG)
of NFs, service SLA options, price information and deployment instructions. NFs could either be a basic service
component, as described in the NF Information Base (NFIB), or recursively refer to services in the service
catalogue. The pricing information of a service can be described as a function of the requirements on the
overall graph (i.e. number and location of the end devices) and the functional and non-functional
requirements of its component NFs. Service templates are advertised across MdOs in different administrative
domains using interface I2-C. For instance, the MdO service provider A in Figure 6.4.5-2 can request services
and/or NFs offered by the MdO service provider B and exposed over interface I2-C to provision a certain
service to its customers.
134