Page 135 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 135
ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables 3
6.4.4.2 Development Focus and Research Challenges of 5G SONATA Project
SONATA [Ref.6.4.4-2] [Ref.6.4.4-3] advocates a consistent view of 5G network and compute functions,
encompassing a wide conceptual range of such functionality. SONATA functionality covers the Multi-service
Control layer and partially Integrated Management and Operation layer and the Application and Business
Services Layer. SONATA is also capable of incorporating widely heterogeneous physical resources: various
access networks (esp., radio), aggregation & core networks, software networks, data centre networks and
mobile edge computing clouds.
A multi-service Control layer is responsible for the creation, operation, and control of multiple dedicated
communication network services running on top of a common infrastructure. SONATA’s functionality for this
layer includes: infrastructure abstraction, infrastructure capability discovery, catalogues and repositories,
large number of service and resource orchestration functions as plugins, information management
functionality and enablers for automatic re-configuration of running services.
The Business Function Layer maintains 5G application-related functions, organized in Repositories, and
DevOps tools necessary for the creation and deployment of services. SONATA’s functionality for this layer
includes DevOps functionality: Catalogues, Monitoring data analysis tools, Testing tools, Packaging tools,
Editors and basic functionality for Application & Service programmability.
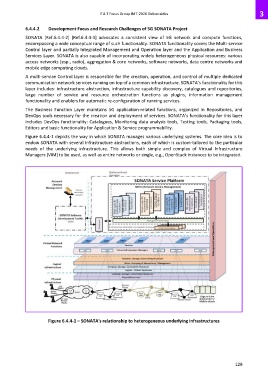
Figure 6.4.4-1 depicts the way in which SONATA manages various underlying systems. The core idea is to
endow SONATA with several infrastructure abstractions, each of which is custom-tailored to the particular
needs of the underlying infrastructure. This allows both simple and complex of Virtual Infrastructure
Managers (VIM) to be used, as well as entire networks or single, e.g., OpenStack instances to be integrated.
Figure 6.4.4-1 – SONATA's relationship to heterogeneous underlying infrastructures
129