Page 139 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 139
ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables 3
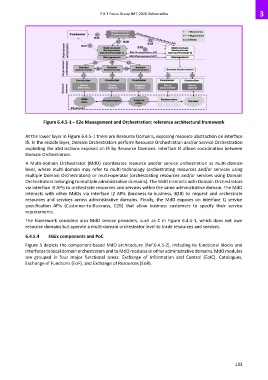
Figure 6.4.5-1 – E2e Management and Orchestration: reference architectural framework
At the lower layer in Figure 6.4.5-1 there are Resource Domains, exposing resource abstraction on interface
I5. In the middle layer, Domain Orchestrators perform Resource Orchestration and/or Service Orchestration
exploiting the abstractions exposed on I5 by Resource Domains. Interface I4 allows coordination between
Domain Orchestrators.
A Multi-domain Orchestrator (MdO) coordinates resource and/or service orchestration at multi-domain
level, where multi-domain may refer to multi-technology (orchestrating resources and/or services using
multiple Domain Orchestrators) or multi-operator (orchestrating resources and/or services using Domain
Orchestrators belonging to multiple administrative domains). The MdO interacts with Domain Orchestrators
via interface I3 APIs to orchestrate resources and services within the same administrative domain. The MdO
interacts with other MdOs via interface I2 APIs (business-to-business, B2B) to request and orchestrate
resources and services across administrative domains. Finally, the MdO exposes on interface I1 service
specification APIs (Customer-to-Business, C2B) that allow business customers to specify their service
requirements.
The framework considers also MdO service providers, such as C in Figure 6.4.5-1, which does not own
resource domains but operate a multi-domain orchestrator level to trade resources and services.
6.4.5.4 5GEx components and PoC
Figure 5 depicts the component-based MdO architecture [Ref.6.4.5-2], including its functional blocks and
interfaces to local domain orchestrators and to MdO modules in other administrative domains. MdO modules
are grouped in four major functional areas: Exchange of Information and Control (EoIC), Catalogues,
Exchange of Functions (EoF), and Exchange of Resources (EoR).
133