Page 73 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 73
Core network aspects 1
5) The DAN elements in a fragmented network may indirectly receive the emergency data, e.g.,
through a patrol car carrying the data from a non-disaster area.
6) The DAN elements deliver the data to many and unspecified people in the fragmented network.
7) Users in the fragmented network can share information with others through the DAN elements that
have storage and processing capabilities.
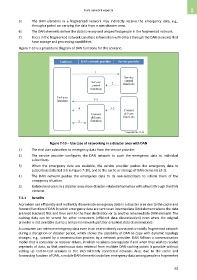
Figure 7-10 is a procedural diagram of DAN functions for this scenario.
Figure 7-10 – Use case of networking in a disaster area with DAN
1) The end user subscribes to emergency data from the service provider.
2) The service provider configures the DAN network to push the emergency data to individual
subscribers.
3) When the emergency data are available, the service provider pushes the emergency data to
subscribers (labelled 3-1 in Figure 7-10), and to the cache or storage of DAN elements (3-2).
4) The DAN network pushes the emergency data to its non-subscribers to inform them of the
emergency situation.
5) Isolated end users in a disaster area share disaster-related information with others through the DAN
element.
7.5.1 Benefits
A provider can efficiently and resiliently disseminate emergency data in a disaster area due to the cache and
forward function of DAN in which emergency data are sent to an intermediate DAN element where the data
are kept (cached) first and then sent to the final destination or to another intermediate DAN element. The
caching data can be served for other consumers (efficient data dissemination) even when the original
provider is not available due to a temporal network partition (resilient data dissemination).
A consumer can retrieve emergency data even in an intermittently connected or totally fragmented network
during a disruption or disaster period, which shows the capability of DAN to cope with dynamic topology
changes, e.g., caused by a reconstruction process by a network provider. DAN follows a communication
model that is consumer or receiver driven, in which receivers can regulate if and when they wish to receive
segments of data, so that continuous data retrieval from multiple DAN caching points is possible without
setting up end-to-end sessions in the intermittently connected network. Also, due to the cache and
forwarding function of DAN, a mobile DAN element can deliver emergency data among people in fragmented
63