Page 69 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 69
Core network aspects 1
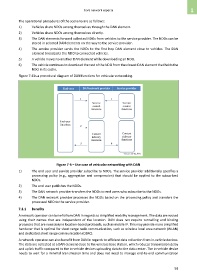
The operational procedures of the scenario are as follows:
1) Vehicles share NDOs among themselves through the DAN element.
2) Vehicles share NDOs among themselves directly.
3) The DAN elements forward collected NDOs from vehicles to the service provider. The NDOs can be
stored in selected DAN elements on the way to the service provider.
4) The service provider sends the NDOs to the first hop DAN element close to vehicles. The DAN
element broadcasts the NDO to connected vehicles.
5) A vehicle moves to another DAN element while downloading an NDO.
6) The vehicle continues to download the rest of the NDO from the closest DAN element that holds the
NDO in its cache.
Figure 7-6 is a procedural diagram of DAN functions for vehicular networking.
Figure 7-6 – Use case of vehicular networking with DAN
1) The end user and service provider subscribe to NDOs. The service provider additionally specifies a
processing policy (e.g., aggregation and compression) that should be applied to the subscribed
NDOs.
2) The end user publishes the NDOs.
3) The DAN network provider transfers the NDOs to end users who subscribe to the NDOs.
4) The DAN network provider processes the NDOs based on the processing policy and transfers the
processed NDO to the service provider.
7.3.1 Benefits
A network operator can benefit from DAN in regards to simplified mobility management. The data are routed
using their names that are independent of the location. DAN does not require tunnelling and binding
processes that are necessary in location-based protocols, such as mobile IP. This may provide more simplified
handover that is optimal for short range radio communication, such as wireless local area network (WLAN)
and dedicated short range communication (DSRC).
A network operator can also benefit from DAN in regards to efficient data collection from in-vehicle devices.
The data are collected at a DAN element close to the wireless base station, which reduces transmission delay
and uplink traffic compared to the in-vehicle devices uploading data to the data center. The in-vehicle device
needs to wait for a minimal transmission time and does not need to manage end-to-end communication
59