Page 358 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 358
1 Core network aspects
architecture defines new FEs characterized by these multi-connection functions. Especially, in the MUE, the
multi-connection terminal control functional entity (MTC-FE) is added to support the interaction between
the MUE and the network.
Additionally, the multi-connection control function (MCF) contains the multi-connection user profile
functional entity (MUP-FE), the multi-connection policy control functional entity (MPC-FE), the multi-
connection coordination functional entity (MC-FE), the multi-connection registration functional entity (MR-
FE) and the multi-connection media function (MMF).
Therefore, the resource IDs defined at the MUE are recommended to be related to these multi-connection
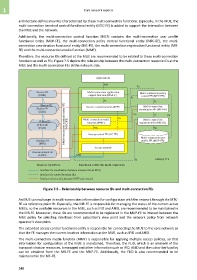
functions as well as FEs. Figure 7-5 depicts the relationship between the multi-connection resource IDs at the
MUE and the multi-connection FEs at the network side.
Applications
ANI
Pa
Service ID Multi-connection application Multi-connection policy
(SVID) support function (MAS-F) control FE (MPC-FE)
Ps
As Pc
Multi-connection terminal control FE (MTC-FE) Multi-connection media Sa registration FE (MR-FE)
Multi-connection
Session ID Service control function (SCF) coordination FE (MC-FE)
(SEID) Cm Cr Pu
Multi-connection
function (MMF)
IP flow ID
(FLID) Ma Ru
profile FE (MUP-FE)
Interface ID Access control FE (AC-FE) Multi-connection user
(IFID)
Access network
Access network ID
(ANID) UNI
Rt Y.2252(12)_F7-5
Resource identifiers Functional entities for multi-connection
Interface for coordination between resource IDs at MUE
Interface for control between FEs
Interface relationship between MUE and network
Figure 7-5 – Relationship between resource IDs and multi-connection FEs
An MUE can exchange its multi-connection information for configuration with the network through the MTC-
FE via reference point Rt. Especially, the MR-FE is responsible for managing the status of the current active
MUEs, so the available resources in the MUE, such as IFID and ANID, are recommended to be maintained in
the MR-FE. Moreover, these IDs are recommended to be registered in the MUP-FE to interact between the
MUE policy for selecting interfaces from subscriber's view point and the network policy from network
operator's view point.
The extended access control functional entity is responsible for connecting the MUE to the core network so
that the FE manages the current location information at the MUE, such as IFID and ANID.
The multi-connection media function (MMF) is responsible for applying multiple access policies, so that
information for configuration at the MUE is maintained. Therefore, the FLID, which is an element of the
transport stratum resources, is managed and other information such as IFID, ANID and the subscriber's policy
can be obtained from the MR-FE and the MUP-FE. Additionally, the FLID is also recommended to be
maintained in the MC-FE.
348